March 27, 2025 · 15 min read
The Role of AI in Government Digital Transformation: The Future of Smart Governance

Shaimaa Badawi

Artificial intelligence is transforming how governments operate. From AI-powered urban planning to predictive analytics in healthcare and education, top digital nations are setting the pace for smart governance. This article explores how AI enables data-driven policymaking, strengthens transparency, supports smart cities, and addresses ethical and cybersecurity challenges.
How is artificial intelligence driving the future of smart governance?
Artificial intelligence is reshaping the future of smart governance by transforming how governments operate, make decisions, and engage with citizens. AI-driven digital transformation enables more efficient, transparent, and data-driven governance, allowing public institutions to respond proactively to societal needs.
Enhancing government efficiency and decision-making
Governments are leveraging AI to automate administrative tasks, optimize resource allocation, and improve decision-making. AI-powered analytics can process vast amounts of data to identify patterns, predict policy outcomes, and streamline bureaucratic workflows. Lessons from the digital transformation in project management can guide public sector leaders as they integrate AI to boost efficiency, visibility, and outcome tracking across government initiatives.
Predictive governance and AI-driven policy formulation
AI enables predictive governance by analyzing historical data and real-time inputs to forecast social trends, economic shifts, and public needs. Predictive models help governments anticipate crises, allocate resources efficiently, and implement proactive policies.
Smart cities and AI-powered public services
AI is at the core of smart city initiatives, where real-time data processing enhances urban infrastructure, transportation, and public safety. AI-powered traffic management systems, waste management automation, and smart surveillance improve city planning and resource efficiency. Governments must explore how AI is shaping the future of smart cities to stay ahead in infrastructure innovation and citizen services.
AI for transparency and public trust
AI-driven automation reduces human intervention in governance, minimizing opportunities for corruption and ensuring more transparent processes. Blockchain-integrated AI models enhance procurement integrity, making financial transactions traceable and fraud-resistant. Governments worldwide are adopting AI-powered chatbots and digital assistants to provide instant access to public information, boosting citizen engagement and trust.
How does AI automate government services and enhance operational efficiency?
AI-driven governance enables public institutions to process vast amounts of data, respond faster to societal needs, and improve resource allocation.
AI-driven decision-making
Governments handle massive datasets, making AI a powerful tool for extracting insights and predicting trends. AI-driven decision-making systems analyze historical and real-time data to improve policy formulation, crisis management, and regulatory enforcement. Governments are beginning to apply models similar to those used for AI in investment decision-making.
- Predictive analytics for policy planning: AI models assess past data to predict future trends, allowing governments to anticipate social, economic, and environmental challenges.
- Risk assessment in public administration: AI helps authorities assess risks related to fraud, security threats, and economic fluctuations. AI-powered fraud detection tools in tax agencies have reduced fraudulent claims and improved revenue collection.
- Personalized public services: AI tailors services based on individual needs. In healthcare, AI-driven systems analyze patient data to recommend personalized treatment plans and optimize medical resource distribution.
Automating government services
AI-driven automation eliminates manual inefficiencies, making government services more accessible, reliable, and cost-effective.
- AI chatbots for public assistance: Many governments use AI chatbots to handle citizen inquiries, reducing wait times and freeing up human resources. Dubai’s "Rashid" AI assistant provides instant responses to residents’ questions about visas, licenses, and services.
- E-government portals with AI automation: AI streamlines administrative tasks such as tax filing, business registration, and permit approvals.
- Robotic process automation (RPA) in bureaucracy: Governments use RPA to handle repetitive tasks like document verification and data entry.
Enhancing operational efficiency
AI optimizes how governments allocate resources, reducing waste and improving productivity.
- AI in budgeting and financial management: Machine learning models detect inefficiencies in government spending, flagging areas where budgets can be optimized. Public finance agencies can take cues from the private sector’s evolution from traditional banking to fintech when integrating AI into their financial operations.
- Optimizing workforce management: AI tools assist in workforce planning by analyzing productivity patterns and optimizing employee schedules. AI-powered systems that cut down on time-consuming meetings directly contribute to the ROI of reduced meeting time in terms of staff availability and administrative savings.
- Energy and infrastructure optimization: Smart AI systems manage energy consumption in public buildings, reduce waste, and enhance sustainability efforts. AI-powered smart grids optimize electricity distribution, cutting operational costs.
How are governments using AI to build smarter cities?
Governments worldwide are integrating artificial intelligence into urban infrastructure to create smarter, more sustainable cities.
1. AI in urban planning
AI is revolutionizing city planning in the Gulf, optimizing land use, infrastructure, and public services.
- NEOM, Saudi Arabia: NEOM, KSA’s $500 billion AI-powered smart city, integrates AI in traffic management, security, and sustainable resource allocation. The city is fully powered by AI-driven renewable energy systems.
- Lusail, Qatar: AI-driven urban planning tools in Lusail optimize water usage, waste collection, and public transport based on real-time data.
- Masdar City, UAE: One of the world’s most sustainable urban projects, Masdar City uses AI to analyze energy consumption, air quality, and traffic patterns, ensuring minimal environmental impact.
2. AI in transportation
Traffic congestion is a major challenge in Gulf cities. AI-powered solutions are optimizing traffic flow, public transport, and ride-sharing systems.
- Riyadh’s AI traffic management system: Saudi Arabia has deployed AI-driven traffic solutions in Riyadh to adjust signals in real time, predict congestion, and improve road safety.
- Dubai’s smart traffic monitoring: Dubai’s Roads and Transport Authority (RTA) integrates AI to optimize bus routes, metro schedules, and reduce congestion using predictive analytics.
- Doha metro AI integration: AI controls automated train schedules, adjusts capacity based on demand, and minimizes delays, making Qatar’s metro system one of the most efficient in the region.
Autonomous vehicles and AI-powered mobility:
- The UAE and KSA are testing self-driving taxis and autonomous buses for future public transport.
- Abu Dhabi has already launched AI-powered driverless shuttles, enhancing urban mobility.
3. AI in public safety and crime prevention
Gulf cities are enhancing security and emergency response with AI-powered surveillance and predictive policing.
- Makkah’s smart surveillance system: AI-powered facial recognition cameras monitor large crowds, especially during Hajj, ensuring safety and efficient crowd control.
- Dubai Police AI crime prediction: Dubai Police use AI algorithms to predict crime hotspots, optimize patrol routes, and analyze security threats before they occur.
- Saudi Arabia’s AI emergency response: AI helps the Saudi Civil Defense predict fire outbreaks and natural disaster risks, improving response times.
4. AI in energy and sustainability
Governments in the GCC are integrating AI to reduce carbon footprints, optimize resource usage, and improve energy efficiency.
- Saudi Aramco’s AI for energy efficiency: AI optimizes Saudi Aramco’s oil and gas operations, reducing emissions and improving production sustainability. Its AI-driven approach mirrors the broader digital transformation in the oil and gas industry, where smart systems enhance efficiency and sustainability.
- Dubai’s AI-managed smart grid: AI regulates energy distribution across Dubai’s public infrastructure, reducing electricity waste and integrating solar energy efficiently.
- Qatar’s AI for water conservation: AI-driven desalination plants optimize water production and detect leaks in municipal pipelines, reducing wastage.
5. AI in public services and citizen engagement
AI is making Gulf city services more efficient and citizen-centric, reducing bureaucracy and enhancing accessibility.
- Absher AI platform (KSA): The Saudi government’s AI-driven e-government portal, Absher, streamlines visa renewals, business registrations, and civil services.
- Dubai’s AI chatbot "Rashid": Dubai’s government uses an AI-powered virtual assistant to answer public inquiries related to permits, services, and regulations.
- Kuwait’s AI-based public complaint system: AI analyzes resident complaints, ensuring quicker resolutions for municipal issues like waste management and traffic concerns.
6. AI in infrastructure maintenance and smart buildings
AI is improving infrastructure resilience in GCC cities by predicting maintenance needs and optimizing building energy use.
- Jeddah’s smart flood management system: AI predicts flash floods and controls drainage networks to prevent disasters.
- Doha’s AI-driven smart buildings: AI regulates cooling, lighting, and ventilation in high-rise buildings, improving sustainability.
- UAE’s predictive maintenance for roads and bridges: AI monitors the condition of roads, bridges, and tunnels, identifying weaknesses before they lead to costly repairs.
What are the biggest ethical challenges in AI-driven government transformation?
AI is transforming how governments operate, but its adoption brings significant challenges. Ethical concerns, regulatory gaps, and cybersecurity risks must be addressed to ensure fair, secure, and transparent AI governance.
1. Ethical challenges
Governments must ensure that AI-driven decisions are fair, unbiased, and transparent while maintaining public trust.
Algorithmic bias and discrimination
- AI models can reinforce societal biases if trained on biased historical data.
- In law enforcement, AI-driven predictive policing may disproportionately target specific communities, raising ethical concerns.
- The UAE and KSA are developing AI ethical guidelines to prevent discriminatory outcomes in AI decision-making.
AI and citizen privacy
- Governments collect vast amounts of data through AI surveillance, raising privacy concerns.
- In smart cities like NEOM (Saudi Arabia) and Dubai Smart City, AI-powered cameras track movement, prompting concerns about mass surveillance.
- Striking a balance between security and privacy rights remains a challenge.
AI replacing human oversight
- Automated decision-making in social welfare, immigration, and law enforcement raises concerns about lack of human accountability.
- In KSA, AI-driven automated traffic violation systems have streamlined law enforcement but also sparked debates on appeals and errors in AI enforcement.
2. Regulatory challenges
Lack of global AI standards
- Countries are racing to implement AI regulations, but a lack of international standards leads to inconsistencies.
- The EU AI Act is among the first comprehensive AI laws, but Gulf countries are still developing AI-specific legal frameworks.
AI in government decision-making
- AI automates welfare, taxation, and security, but without clear regulations, it can lack transparency.
- Kuwait and Bahrain are exploring AI-based taxation systems, but concerns remain over how decisions are made and who is accountable.
Data ownership and cross-border AI regulations
- AI-driven government systems rely on cross-border data sharing, raising concerns about who owns citizen data.
- Qatar and UAE have strict data localization laws, requiring government data to be stored within national borders.
3. Cybersecurity challenges
As AI is integrated into defense, finance, healthcare, and governance, it increases cybersecurity vulnerabilities. Addressing cybersecurity in the digital era becomes crucial to protect public data, digital infrastructure, and AI-driven services.
AI-powered cyberattacks
- AI can be used to automate and scale cyberattacks, posing risks to national security.
- In 2022, Saudi Arabia's National Cybersecurity Authority reported an increase in AI-driven cyber threats, prompting investments in AI-based threat detection.
Government data breaches and hacking risks
- AI-driven smart city infrastructure is vulnerable to hacking.
- Dubai and Riyadh have deployed AI cybersecurity systems to protect municipal networks, financial transactions, and e-government portals from cyber threats.
Deepfakes and AI-generated disinformation
- AI can be used to create deepfake videos or fake government messages, leading to public misinformation.
- The UAE is working on AI-powered fact-checking tools to combat AI-generated fake news targeting government policies.
How does AI enable data-driven policymaking in public administration?
Governments are increasingly turning to artificial intelligence to make better decisions and regain public trust. AI enables data-driven policymaking by turning raw data into actionable insights, while also improving transparency by automating processes, reducing human error, and making information more accessible.
AI for smarter, data-backed policies
Governments collect enormous amounts of data, but without the right tools, most of it goes unused. Their research initiatives and pilot programs are also benefiting from AI tools that streamline research and project management.
- Real-time insights for faster decisions
AI systems analyze real-time data from public services, transportation, healthcare, and education to help leaders respond faster. For instance, South Korea’s Smart Government platform uses AI to track citizen feedback and adjust services based on real-time input. - Predictive analytics to anticipate needs
Instead of reacting to problems, AI helps governments forecast issues before they happen. In the UAE, predictive models in public health have helped allocate hospital resources more efficiently during disease outbreaks. - Performance tracking for better governance
AI dashboards visualize key performance indicators (KPIs) for government programs. In Saudi Arabia, Vision 2030 initiatives use AI-powered analytics to monitor progress on national transformation goals.
AI and transparency
One of the biggest benefits of AI in governance is its ability to improve transparency, both in how decisions are made and how resources are used.
- Automated records leave no room for manipulation
When AI automates processes like procurement, financial auditing, or licensing, it reduces human intervention, which lowers the risk of corruption. Committees across the public sector are exploring AI documentation in government committees to improve record-keeping, follow-ups, and institutional memory. Estonia’s X-Road platform uses AI and blockchain to track public transactions securely, creating a tamper-proof audit trail. - AI in open data initiatives
AI systems can automatically analyze, categorize, and publish public data, making it easier for citizens to access information. The Dubai Pulse platform, for example, uses AI to help residents explore government performance data without technical barriers. - AI-powered fraud detection
AI detects irregularities in financial transactions that manual audits might miss. In India, AI tools helped flag fraudulent subsidy claims, saving billions in public funds.
Real-time citizen feedback loops
AI tools process data from online forums, service portals, and social media to capture public sentiment and track concerns. Using NLP in meetings and stakeholder sentiment analysis helps governments better understand citizen concerns and adapt policies accordingly.
- Sentiment analysis to shape policy
AI systems analyze public opinion on proposed laws or recent changes. This kind of feedback loop makes policy more inclusive and responsive. - Voice of the citizen in real time
Governments in the GCC, like Bahrain and Qatar, are experimenting with AI chatbots that gather citizen complaints, flag urgent issues, and route them directly to relevant departments, helping resolve problems before they escalate.
How does leading digital nations ensure ethical governance?
As governments adopt artificial intelligence to improve services and decision-making, the need for clear, enforceable AI regulations has become urgent. Leading digital nations are now developing frameworks that prioritize transparency, fairness, and accountability in AI systems used for public governance.
1. The European Union
The EU AI Act is the world’s first comprehensive AI law, offering a model for other nations. It classifies AI systems by risk level (unacceptable, high, limited, or minimal) and imposes stricter rules on those used in sensitive areas like education, law enforcement, or social services.
- Key requirements for high-risk AI:
Governments using AI for decisions like welfare eligibility or school admissions must ensure their systems are transparent, auditable, and free from bias. - Ban on harmful use cases:
The Act prohibits social scoring systems and real-time facial recognition in public spaces, except under specific, justified circumstances. - Implication for GCC countries:
As the EU is a major trade partner, GCC nations working on cross-border AI services are starting to align some of their standards with the EU model to maintain interoperability.
2. Singapore
Singapore balances innovation and regulation through its Model AI Governance Framework, which is voluntary but widely adopted.
- Explainable AI:
Public agencies must be able to explain how AI systems arrive at decisions, especially when used in housing, immigration, or healthcare. - Risk-based approach:
Agencies are encouraged to evaluate how decisions impact citizens and ensure that sensitive decisions still include human oversight. - Government role:
Singapore’s AI Verify Toolkit, an open-source testing tool, helps agencies self-assess whether their AI systems meet ethical guidelines before deployment.
3. United Arab Emirates
The UAE has launched a national strategy for AI with a strong ethics and governance component, positioning itself as a regional leader.
- AI ethics guidelines:
The UAE’s guidelines cover transparency, fairness, and inclusiveness, and are applied across smart city programs, education, and security. - Minister of AI:
The UAE is the first country with a Minister of State for Artificial Intelligence, tasked with aligning technology initiatives with ethical and sustainable goals. - Smart Dubai:
Smart Dubai uses an AI Ethics Self-Assessment Tool that helps government departments audit their own systems and ensure alignment with public values.
4. Saudi Arabia
Saudi Arabia’s Saudi Data and Artificial Intelligence Authority (SDAIA) is developing national regulations to govern the safe use of AI in both public and private sectors.
- AI principles charter:
SDAIA’s charter outlines six guiding principles, including privacy, fairness, safety, and accountability. - AI in government services:
AI systems used in e-government portals like Absher are being reviewed for ethical and legal compliance, especially those involving facial recognition and data profiling. - Alignment with global standards:
Saudi Arabia is collaborating with international organizations like OECD and ISO to ensure its regulatory framework aligns with global best practices.
5. United States
While the U.S. lacks a single federal AI law, it regulates AI through sector-specific policies in health, finance, and defense.
- Blueprint for an AI bill of rights:
This document offers guidelines for safe, explainable, and privacy-respecting AI, especially in public service contexts like education and law enforcement. - Audits and redress mechanisms:
Agencies using AI for decision-making are encouraged to offer appeal processes, so citizens can challenge unfair or incorrect AI-generated decisions.
How is AI reshaping public sector jobs?
AI is transforming how public employees work. From clerks to policy analysts, public sector roles are being redefined by automation, data analytics, and AI-driven decision support. This shift doesn’t eliminate the need for people; it reshapes the roles they play and raises the bar for new skills.
What’s changing in the public sector workforce?
Governments are automating routine, repetitive tasks (like data entry, scheduling, and basic approvals) to free up time for higher-level work. Civil servants across departments are benefiting from streamlined collaboration by reducing meeting fatigue with AI. This shift is already visible in countries like Estonia and the UAE, where AI handles everything from business license applications to traffic violation processing.
- Job roles are evolving, not disappearing
AI is taking over administrative tasks, but it’s also creating new roles around data governance, digital ethics, cybersecurity, and AI oversight.
For example, a tax auditor may no longer manually review filings but instead supervise AI systems that flag anomalies, then use their judgment to investigate. Public sector agencies are also adopting machine learning in meeting preparation to ensure decision-makers arrive better informed. - Interdisciplinary teams are the new normal
Public sector teams now include data scientists, tech-savvy analysts, and digital communication experts working alongside traditional civil servants. Governments in Saudi Arabia and Qatar are hiring hybrid roles, people who can speak the language of both public policy and technology.
How can adam.ai help government agencies optimize governance?
adam.ai helps government agencies manage critical meetings with features tailored for transparency, accountability, and strategic alignment.
- Agenda management ensures structured, focused discussions with assigned speakers and time tracking, keeping high-stakes meetings on course.
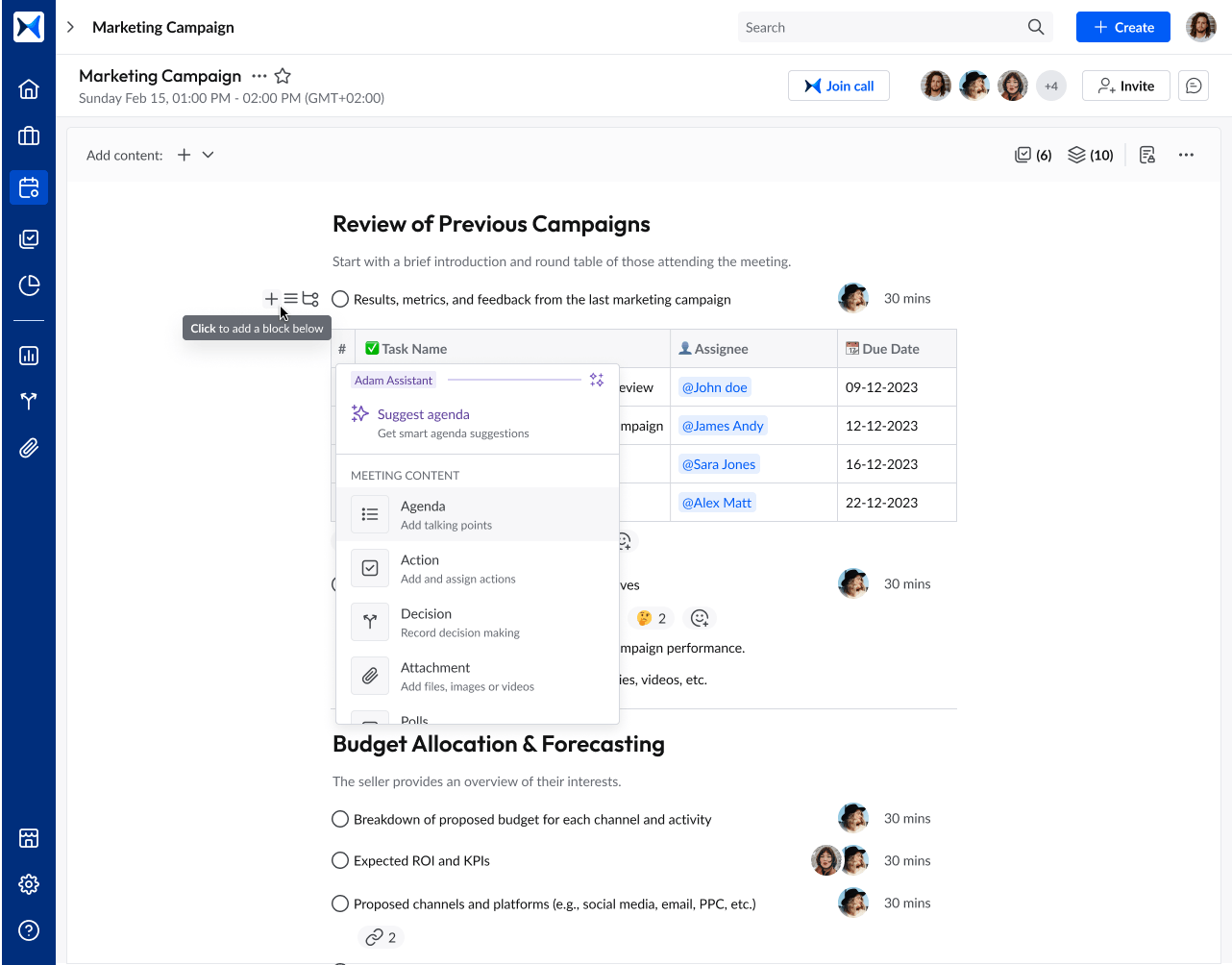
- Content collaboration centralizes documents, reports, and presentations in one secure space, reducing fragmentation across departments.
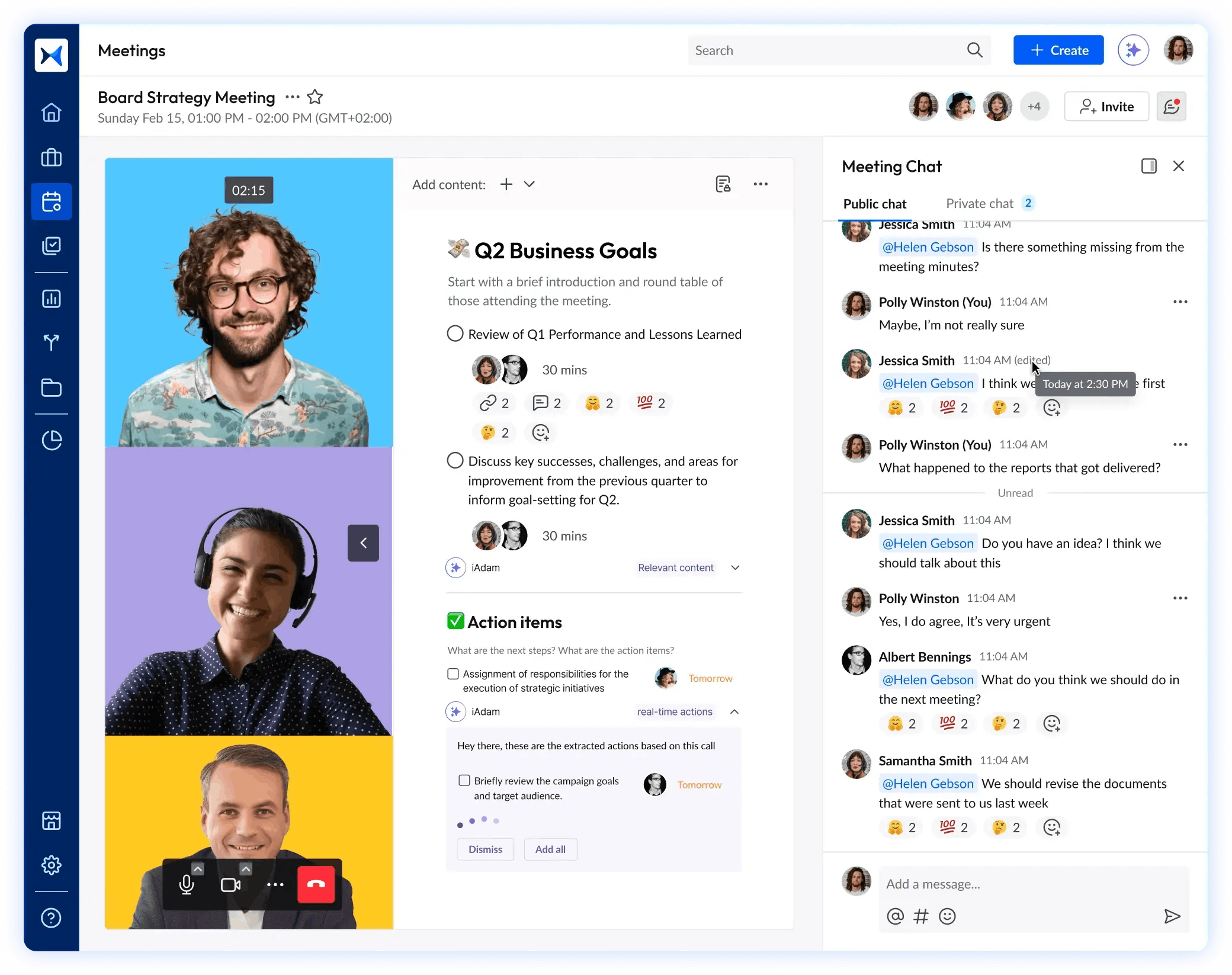
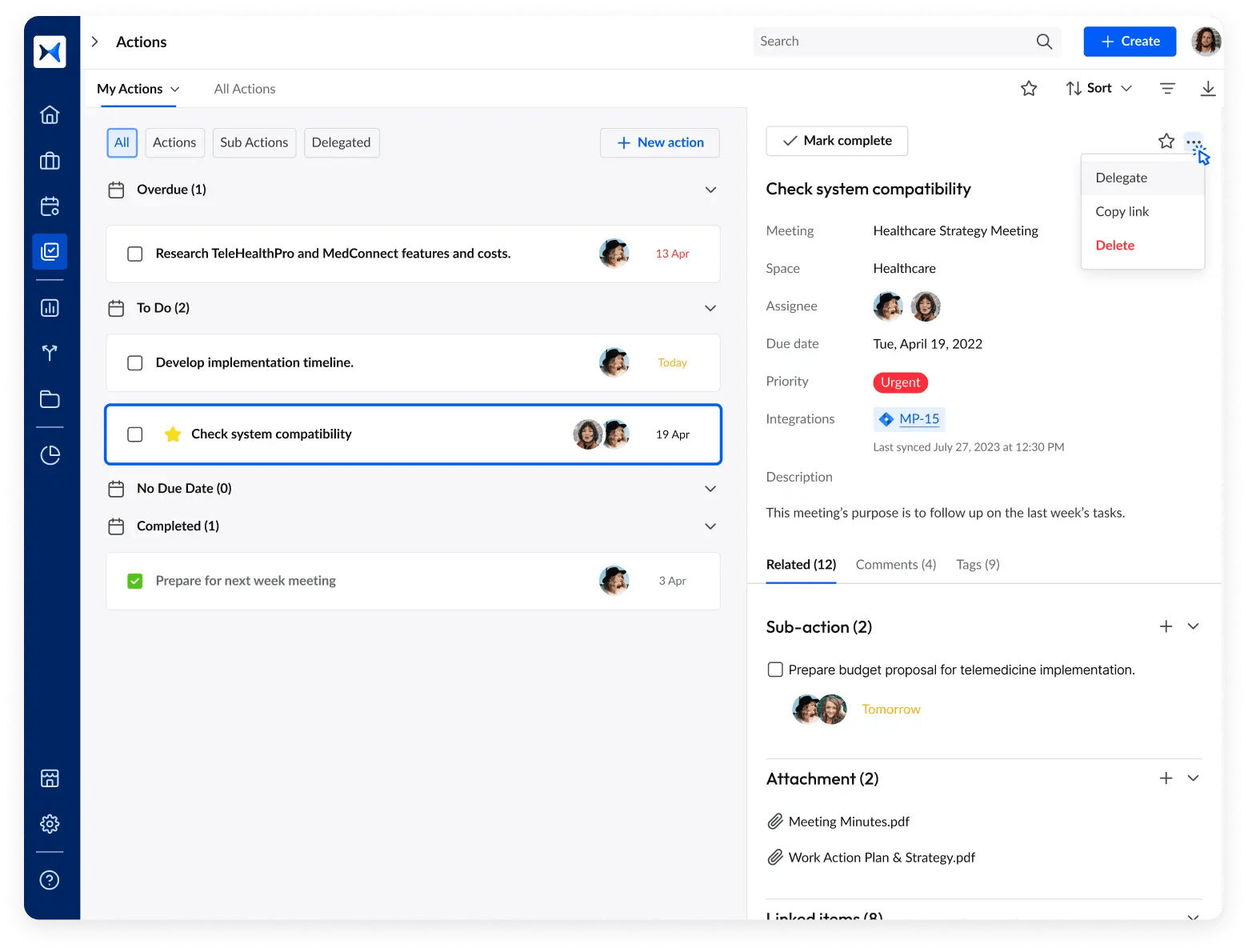
- Action tracking links every decision to a responsible owner and deadline, ensuring follow-through and compliance.
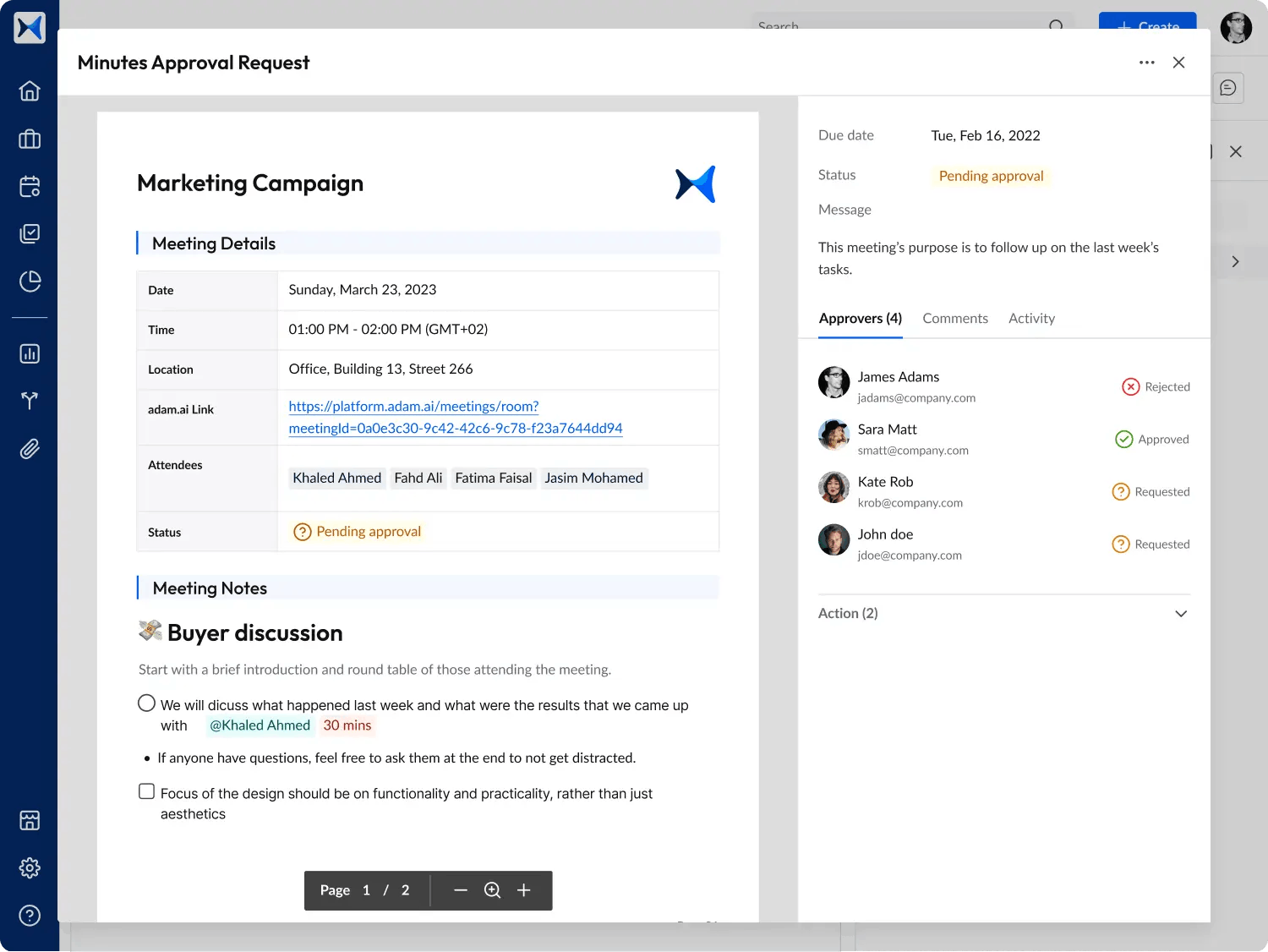
- Meeting minutes are automatically generated, approved, and archived for audit-ready documentation and public accountability.
- Multi-space management allows separate boards, committees, or departments to operate efficiently under one platform, ideal for cross-agency coordination.
- Analytical dashboards offer real-time insights into meeting outcomes, participation, and follow-up rates, driving data-informed governance decisions.
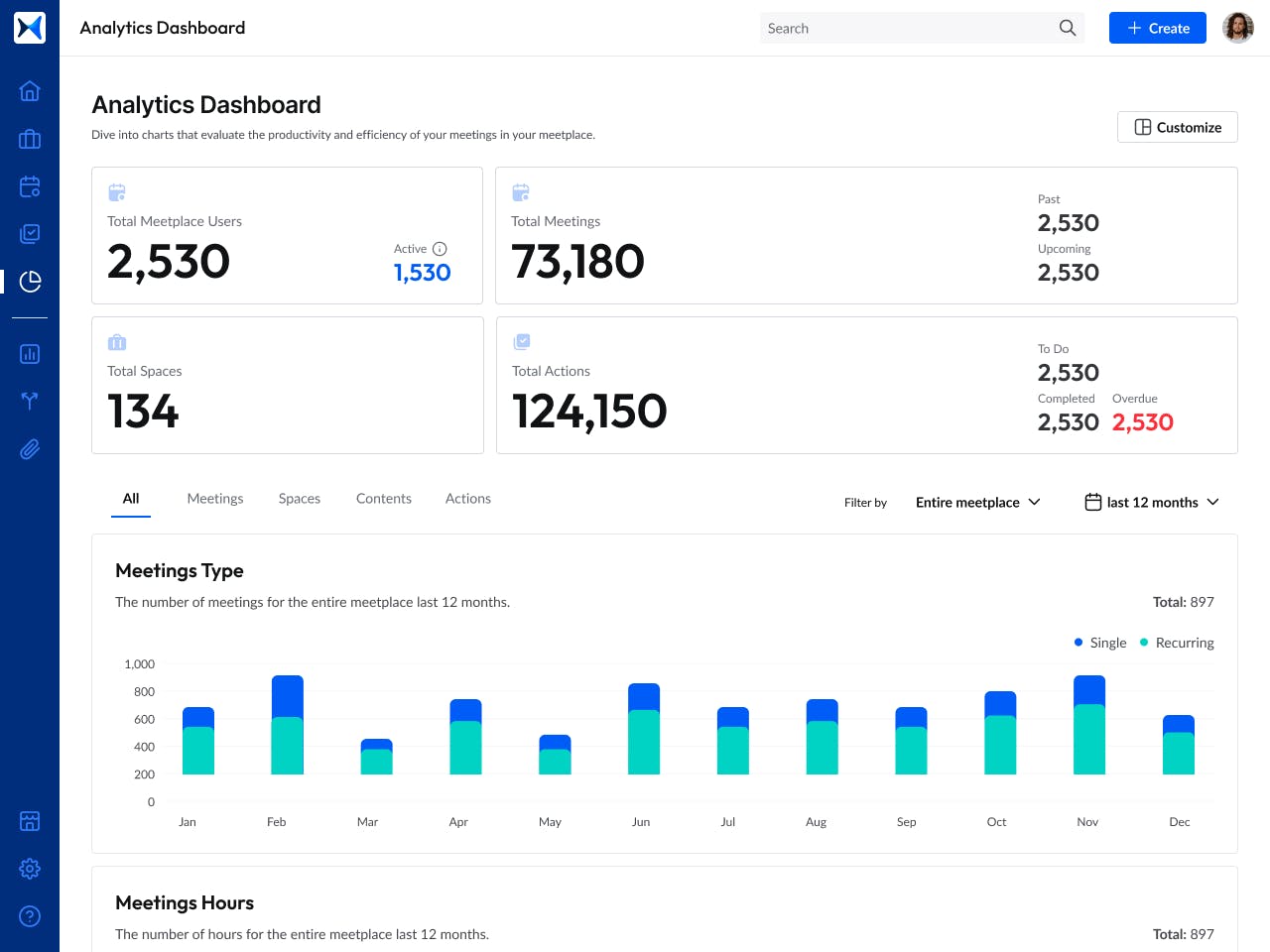
Transform how you conduct critical meetings—From meticulous preparation to effective execution and insightful follow-up, adam.ai integrates comprehensive analytics, full customization, and intuitive interfaces with powerful meeting management tools.
Easy onboarding. Enterprise-grade security. 24/7 dedicated support.
The bottom line
AI is already reshaping public governance. For agencies aiming to lead this transformation, adopting AI is just the start. The real impact comes from combining intelligent technologies with modern platforms to structure decisions, track outcomes, and drive results that citizens can see and trust.
And while there may be multiple solutions available, here is why adam.ai is the meeting management software platform you can trust:
- adam.ai is one of Atlassian Ventures' portfolio companies.
- In the meeting management software category on G2, adam.ai has been ranked a leader and a high performer for successive quarters in the past years.
- adam.ai has been included in the Forrester Report in the AI-enabled meeting technology landscape.
- adam.ai is trusted and used by powerful teams and organizations worldwide for all types of critical meetings, like board, committee, project management, and business development meetings.
- And most importantly, adam.ai integrates with your existing workflow, is SOC2 compliant, provides dedicated support and success, and has a free trial option.
Subscribe to adam.ai blog
Stay ahead with the latest insights—get our newest blog posts, tips, and updates sent straight to your inbox.