December 16, 2024 · 12 min read
Natural Language Processing in Meetings: Understanding Stakeholder Sentiment

Shaimaa Badawi

Understanding stakeholder sentiment is key to making meetings more productive and impactful. Natural Language Processing has transformed how organizations analyze and act on emotions, opinions, and attitudes shared during meetings. In this article, we explore the role of NLP in capturing stakeholder sentiment, the challenges it addresses, and how organizations integrate NLP to enhance meeting outcomes.
What is Natural Language Processing, and how does it function?
Natural Language Processing (NLP) is a field of artificial intelligence (AI) that focuses on the interaction between computers and human language. It enables machines to understand, interpret, and respond to text or speech in ways that are valuable and meaningful. By bridging the gap between human communication and computer understanding, NLP facilitates tasks like text analysis, translation, sentiment analysis, and voice recognition.
How NLP functions
- Text preprocessing
NLP begins with preprocessing the input text or speech. This involves cleaning and normalizing data, such as removing stop words, punctuation, and irrelevant characters, while converting text to a consistent format. - Tokenization
The text is broken into smaller units, or tokens, such as words or phrases. Tokenization helps computers analyze language structures and relationships between words. - Part-of-speech tagging
Each word is tagged with its grammatical role, such as noun, verb, or adjective. This step helps identify sentence structure and meaning. - Named entity recognition (NER)
NLP systems identify and categorize entities in the text, such as names, dates, or locations. This is crucial for extracting actionable information from data. - Sentiment analysis
NLP uses algorithms to determine the emotional tone or sentiment behind the text, positive, negative, or neutral. This helps in understanding stakeholder opinions and feedback. - Parsing and syntax analysis
By analyzing the grammatical structure of sentences, NLP understands the relationships between words, enabling deeper comprehension of the text. - Text summarization and generation
NLP models can generate concise summaries of large documents or even create human-like text responses for chatbots and virtual assistants. - Machine learning and deep learning models
NLP often employs advanced models like transformers (e.g., BERT, GPT) to interpret complex language patterns, handle ambiguities, and learn from context.
Example in action
In a meeting, NLP can transcribe speech into text, analyze the tone of participants, and summarize the discussion. This allows stakeholders to review key points, track decisions, and gauge sentiment efficiently.
Why is understanding stakeholder sentiment critical for successful meetings?
Understanding stakeholder sentiment is essential for ensuring that meetings are productive, collaborative, and aligned with organizational goals. Stakeholder sentiment reflects the emotions, opinions, and attitudes of participants, which can significantly impact the dynamics and outcomes of meetings.
Why understanding stakeholder sentiment matters
- Enhances decision-making
Recognizing how stakeholders feel about issues or proposals allows meeting organizers to address concerns effectively and foster consensus. This leads to more informed and balanced decisions. - Builds trust and collaboration
Acknowledging emotions and perspectives helps create an environment of openness and mutual respect. When participants feel heard, they are more likely to engage constructively. - Identifies hidden concerns
Sentiment analysis can reveal underlying issues or dissatisfaction that may not be explicitly voiced during the meeting. Addressing these concerns early prevents conflicts and ensures smooth execution of decisions. - Supports stakeholder alignment
Meetings often involve diverse participants with different priorities. Understanding sentiment helps bridge gaps between varying perspectives, ensuring everyone works toward a common goal. - Improves meeting effectiveness
By gauging sentiment, organizers can adapt their communication style, pacing, and agenda to keep participants engaged and focused on productive discussions. - Enhances feedback and follow-ups
Understanding sentiment provides actionable insights into how participants perceive meeting outcomes. This enables organizers to refine future meetings and strengthen stakeholder relationships.
Example in practice
In a project kickoff meeting, stakeholder sentiment analysis might reveal hesitations about resource allocation or project timelines. By addressing these concerns during the meeting, organizers can foster confidence, improve morale, and ensure a stronger commitment to the project.
How does NLP enable sentiment analysis in meeting data?
NLP enables sentiment analysis in meeting data by extracting emotions, opinions, and attitudes from text or speech. By leveraging advanced computational techniques, NLP processes unstructured meeting data, like transcriptions or voice recordings, to identify and classify sentiments, providing actionable insights for organizers and participants.
Steps NLP takes to enable sentiment analysis
1. Speech-to-text conversion
- NLP tools use automatic speech recognition (ASR) to convert spoken language during meetings into text. This provides a structured format for further analysis.
- Example: Converting a stakeholder’s verbal feedback into text that can be analyzed for sentiment.
2. Text preprocessing
- Raw text is cleaned and normalized by removing noise, such as filler words or irrelevant phrases, to focus on meaningful content.
- This ensures the accuracy of sentiment analysis, even with informal or fragmented speech.
3. Sentiment classification
- Using algorithms, NLP classifies the text as positive, negative, or neutral. Advanced models go deeper by identifying specific emotions like happiness, frustration, or concern.
- Example: Identifying enthusiasm about a project or concerns over timelines in stakeholder feedback.
4. Aspect-based sentiment analysis (ABSA)
- NLP evaluates sentiments tied to specific aspects of the meeting, such as agenda items, proposed ideas, or decisions.
- This granular approach helps pinpoint which topics elicit positive or negative responses.
5. Contextual understanding
- NLP leverages context-aware models like transformers (e.g., BERT or GPT) to account for nuances, sarcasm, or multi-layered sentiments in speech or text.
- Example: Detecting irony in a stakeholder's comment, ensuring accurate sentiment interpretation.
6. Real-time processing
- Advanced NLP systems can analyze sentiments in real-time, providing live feedback during meetings.
- This helps organizers adjust strategies on the fly, such as clarifying points or addressing concerns promptly.
7. Visualizing sentiment trends
- NLP tools summarize and visualize sentiment trends using dashboards or reports. This allows meeting organizers to track emotional shifts over time and across different meetings.
- Example: Identifying increasing satisfaction with project progress over consecutive meetings.
What challenges do organizations face in analyzing stakeholder sentiment during meetings?
Analyzing stakeholder sentiment during meetings can be complex, requiring advanced tools and processes to capture and interpret nuanced emotional data. Organizations often face several challenges when attempting to understand stakeholder attitudes and emotions effectively.
Key challenges in sentiment analysis
1. Unstructured meeting data
- Issue: Meeting content often consists of unstructured data, including speech, gestures, and informal conversations. Analyzing this data requires robust processing capabilities.
- Impact: Without effective tools, organizations struggle to extract meaningful insights from this data.
2. Ambiguity and context dependence
- Issue: Sentiment can vary based on context, tone, or word choice. Sarcasm, irony, or mixed emotions are particularly difficult for algorithms to interpret.
- Impact: Misinterpretation of sentiments can lead to inaccurate conclusions and ineffective decision-making.
3. Language and cultural nuances
- Issue: Variations in language, slang, and cultural expressions can affect how sentiments are conveyed and understood.
- Impact: Sentiment analysis tools must account for these nuances to avoid bias and inaccuracies.
4. Real-time processing requirements
- Issue: Analyzing sentiment during live meetings demands high computational speed and accuracy.
- Impact: Delays or inaccuracies in real-time processing can hinder the ability to address stakeholder concerns promptly.
5. Integration with existing systems
- Issue: Many organizations struggle to integrate sentiment analysis tools with their existing meeting platforms or workflows.
- Impact: This results in fragmented insights and reduced usability of sentiment data.
6. Data privacy and security
- Issue: Stakeholder feedback often includes sensitive information. Ensuring data privacy while analyzing sentiments can be challenging.
- Impact: Non-compliance with privacy regulations could result in legal and reputational risks.
7. Cost and resource constraints
- Issue: Implementing advanced NLP and sentiment analysis systems requires significant investment in tools, training, and infrastructure.
- Impact: Smaller organizations may struggle to adopt these technologies.
8. Bias in sentiment analysis models
- Issue: Machine learning models may reflect inherent biases in training data, leading to skewed sentiment interpretation.
- Impact: This can result in unfair or incomplete analyses of stakeholder emotions.
Overcoming these challenges
Organizations can address these challenges by:
- Investing in advanced NLP tools with multilingual and context-aware capabilities.
- Training models on diverse datasets to minimize bias.
- Ensuring seamless integration of sentiment analysis tools with meeting management platforms.
- Implementing robust data privacy measures to protect sensitive information.
How can real-time sentiment insights enhance decision-making in meetings?
Real-time sentiment insights provide meeting organizers and participants with immediate feedback on stakeholder emotions, opinions, and concerns. By leveraging these insights, organizations can make more informed and adaptive decisions during the meeting itself, improving collaboration, alignment, and outcomes.
Key benefits
1. Enhanced responsiveness
- How it helps: Real-time analysis allows facilitators to detect and address dissatisfaction, confusion, or disengagement as it happens.
- Example: If stakeholders express hesitation about a proposal, organizers can provide additional information or adjust the plan to resolve concerns immediately.
2. Improved clarity and focus
- How it helps: Understanding sentiments helps prioritize discussion points and identify topics that require further elaboration.
- Example: A sudden spike in negative sentiment towards a project milestone signals the need for more detailed explanations or alternative approaches.
3. Facilitating consensus
- How it helps: Monitoring real-time sentiment reveals areas of agreement or contention, guiding discussions toward solutions that satisfy the majority.
- Example: Positive sentiment trends about specific ideas can be leveraged to build momentum and secure group approval.
4. Prevention of escalation
- How it helps: Identifying negative sentiments early helps prevent conflicts from escalating. Facilitators can diffuse tension through clarifications, empathy, or reframing discussions.
- Example: Addressing frustration about time constraints can refocus the meeting on actionable priorities.
5. Strengthened stakeholder engagement
- How it helps: Acknowledging and responding to participants’ emotions fosters a collaborative atmosphere where stakeholders feel valued.
- Example: Highlighting enthusiasm for certain agenda items boosts morale and encourages active participation.
6. Data-driven adjustments
- How it helps: Real-time sentiment data supports on-the-fly adjustments to meeting flow, such as reallocating time to critical issues or skipping less relevant topics.
- Example: If sentiment trends indicate disengagement during lengthy updates, organizers can shorten updates and move to interactive discussions.
7. Strengthening accountability
- How it helps: Insights into stakeholder reactions ensure decisions align with group sentiment, reducing pushback or resistance in post-meeting follow-ups.
- Example: Positive reactions to a new policy proposal strengthen its credibility and likelihood of successful implementation.
How do organizations integrate NLP tools to automate meeting insights?
Organizations integrate Natural Language Processing (NLP) tools into their meeting workflows to extract actionable insights from large volumes of unstructured data. By automating processes like transcription, sentiment analysis, and summarization, NLP tools streamline meeting management and enhance decision-making efficiency.
Steps to integrate NLP tools
1. Data capture and preprocessing
- How it works: Organizations start by capturing meeting data, including audio, video, and text. NLP tools then preprocess this data, removing noise and standardizing formats for analysis.
- Example: Automatic speech recognition (ASR) tools convert spoken language into text, creating a structured dataset for further processing.
2. Real-time transcription and analysis
- How it works: NLP-powered tools transcribe meetings in real time, tagging speakers and identifying key points for live sentiment analysis.
- Example: Tools like Otter.ai or similar systems provide instant transcripts, allowing participants to review discussions during the meeting.
3. Sentiment analysis integration
- How it works: NLP algorithms analyze the tone and sentiment of participant contributions to gauge engagement, agreement, or concerns.
- Example: Sentiment dashboards display participant emotions throughout the meeting, highlighting areas of contention or enthusiasm.
4. Summarization and action item extraction
- How it works: NLP tools generate concise summaries and extract action items or key decisions from transcripts. This automates a traditionally manual and time-intensive process.
- Example: A meeting summarization tool provides attendees with an email digest of decisions, tasks, and deadlines.
5. Contextual Insights and Recommendations
- How it works: Advanced NLP tools analyze meeting context and historical data to provide insights or recommendations for future actions.
- Example: Suggesting follow-up topics or prioritizing unresolved issues from previous meetings.
6. Integration with meeting management platforms
- How it works: NLP tools are integrated into meeting platforms like adam.ai, enabling seamless workflows from scheduling to documentation and follow-ups.
- Example: Users access NLP-driven insights directly within their meeting management dashboard, eliminating the need for multiple tools.
7. Visualization and reporting
- How it works: Data insights from NLP tools are visualized through charts, graphs, and reports, making it easy to share with stakeholders.
- Example: Weekly reports summarize meeting sentiment trends and action completion rates, helping leaders track progress.
What are some real-world applications of NLP-driven sentiment analysis in stakeholder management?
NLP-driven sentiment analysis has revolutionized stakeholder management by providing actionable insights into emotions, opinions, and attitudes. Organizations leverage this technology across various scenarios to enhance decision-making, foster collaboration, and build stronger stakeholder relationships.
Real-world applications
1. Employee engagement and feedback
- Use case: Analyzing employee surveys, performance reviews, or internal communication channels to gauge morale and address concerns.
- Example: An organization identifies a rise in negative sentiments about workload distribution and implements new task management strategies to boost productivity and satisfaction.
2. Customer relationship management (CRM)
- Use case: Monitoring customer interactions, reviews, and support tickets to assess satisfaction and improve services.
- Example: A retail company uses sentiment analysis to identify frequent complaints about delivery delays, leading to logistics improvements and increased customer loyalty.
3. Investor relations
- Use case: Assessing investor feedback during earnings calls or shareholder meetings to address concerns and reinforce trust.
- Example: Positive sentiment trends around revenue growth discussions help management emphasize financial performance in future communications.
4. Public relations and brand reputation
- Use case: Analyzing social media, news articles, and public statements to understand public perception of the organization or its initiatives.
- Example: A tech company detects negative sentiment surrounding a product launch and responds promptly with clarifications and updates.
5. Project stakeholder engagement
- Use case: Tracking sentiment in project meetings to align team efforts and maintain stakeholder support.
- Example: A construction firm uses sentiment analysis to identify concerns over timelines, leading to adjusted schedules and improved stakeholder confidence.
6. Community feedback in non-profits
- Use case: Gathering insights from beneficiaries and donors to improve programs and campaigns.
- Example: A non-profit analyzes social media feedback to identify enthusiastic responses to a fundraising event, shaping future initiatives.
7. Product development
- Use case: Understanding stakeholder feedback on prototypes or new product features.
- Example: A software company identifies positive sentiment for a new UI feature during focus group discussions and prioritizes its rollout.
8. Government and policy feedback
- Use case: Evaluating public sentiment toward proposed policies or community programs.
- Example: A city council uses sentiment analysis on public meeting transcripts to gauge support for a new transportation plan.
How does adam.ai support stakeholder-centric meetings?
adam.ai offers a suite of intelligent meeting management features that empower organizations to capture stakeholder input, prioritize key topics, and follow through on decisions effectively. Here's how:
- Agenda management: adam.ai helps create focused agendas that prioritize stakeholder concerns and key discussion points. By structuring meetings around clear objectives, it ensures that important topics are addressed in a way that fosters meaningful engagement.
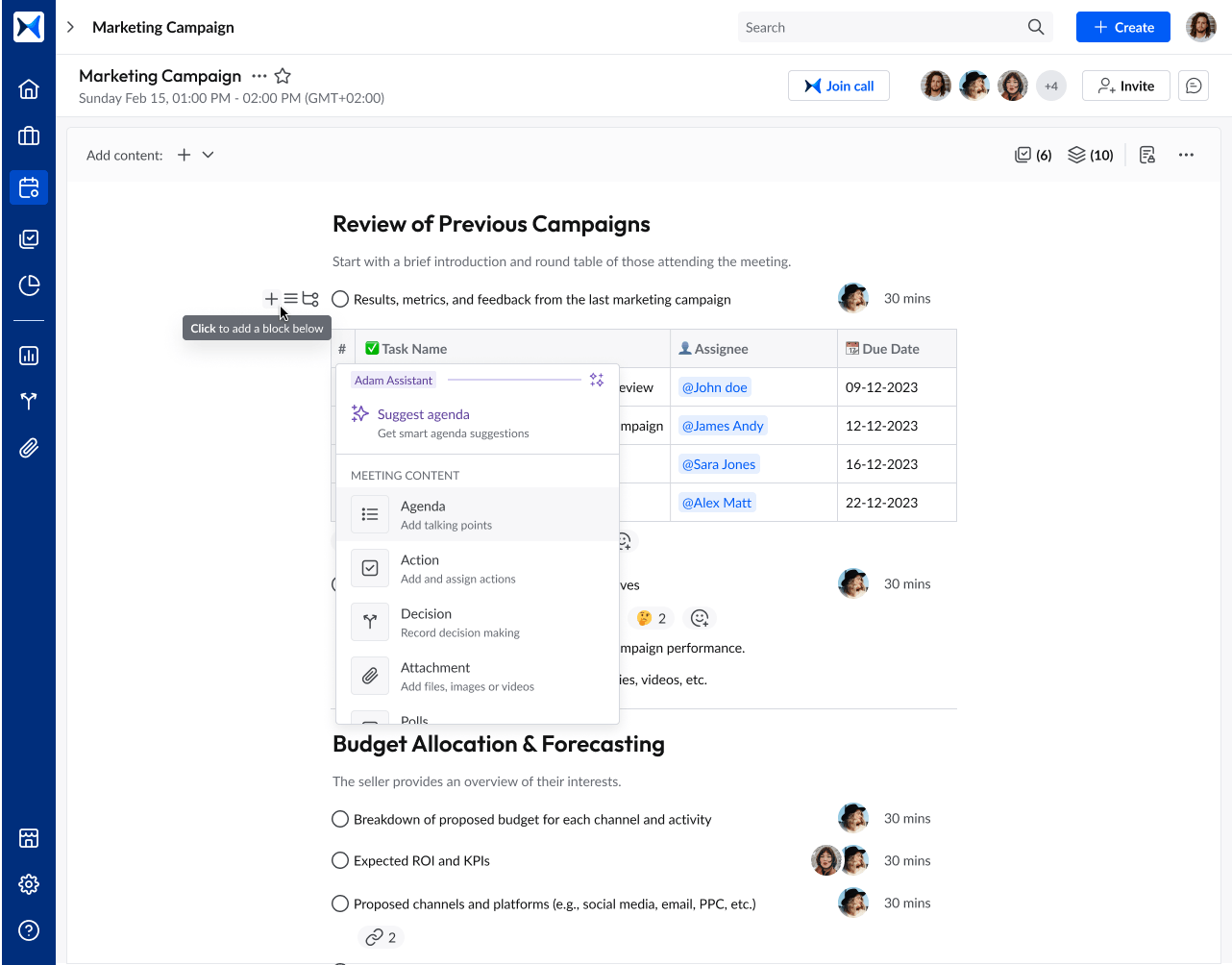
- Content collaboration: The platform centralizes meeting-related documents, allowing teams to share and access materials before and after meetings. This facilitates collaborative discussions where stakeholders’ feedback is integrated seamlessly into decision-making.
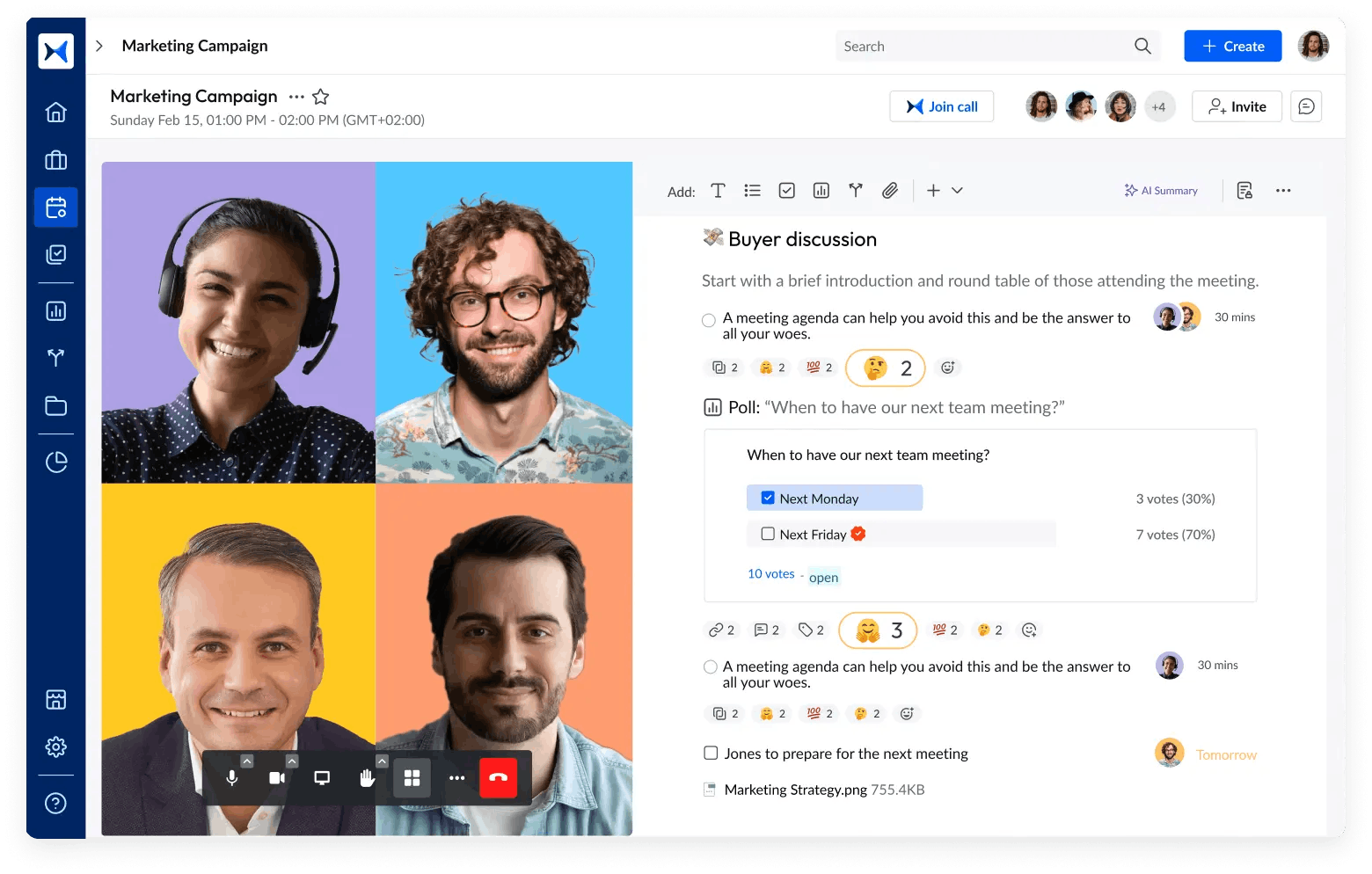
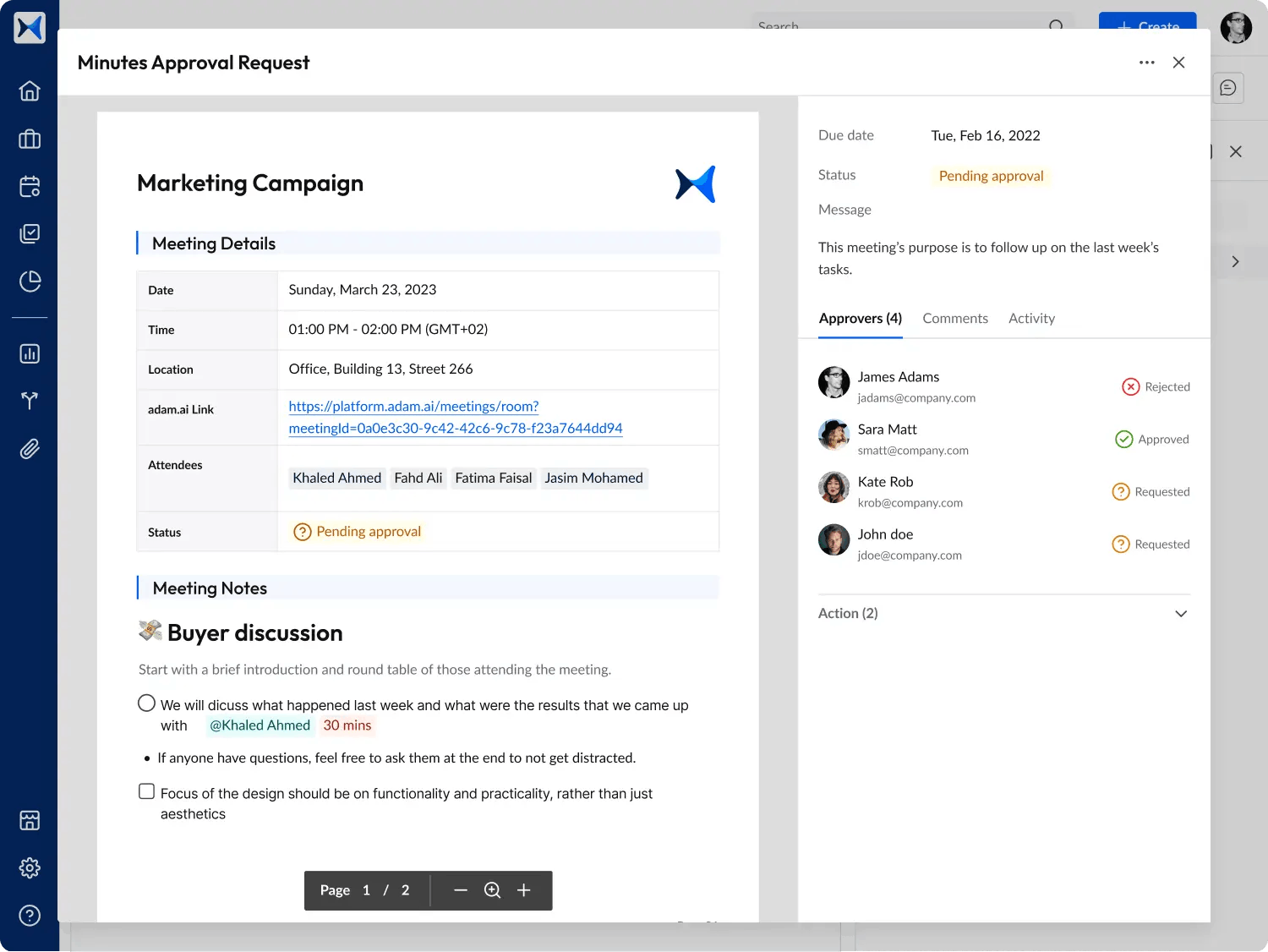
- Meeting minutes: With automated documentation, adam.ai captures the essence of discussions, decisions, and action items. This ensures that all stakeholder input is documented accurately and made actionable.
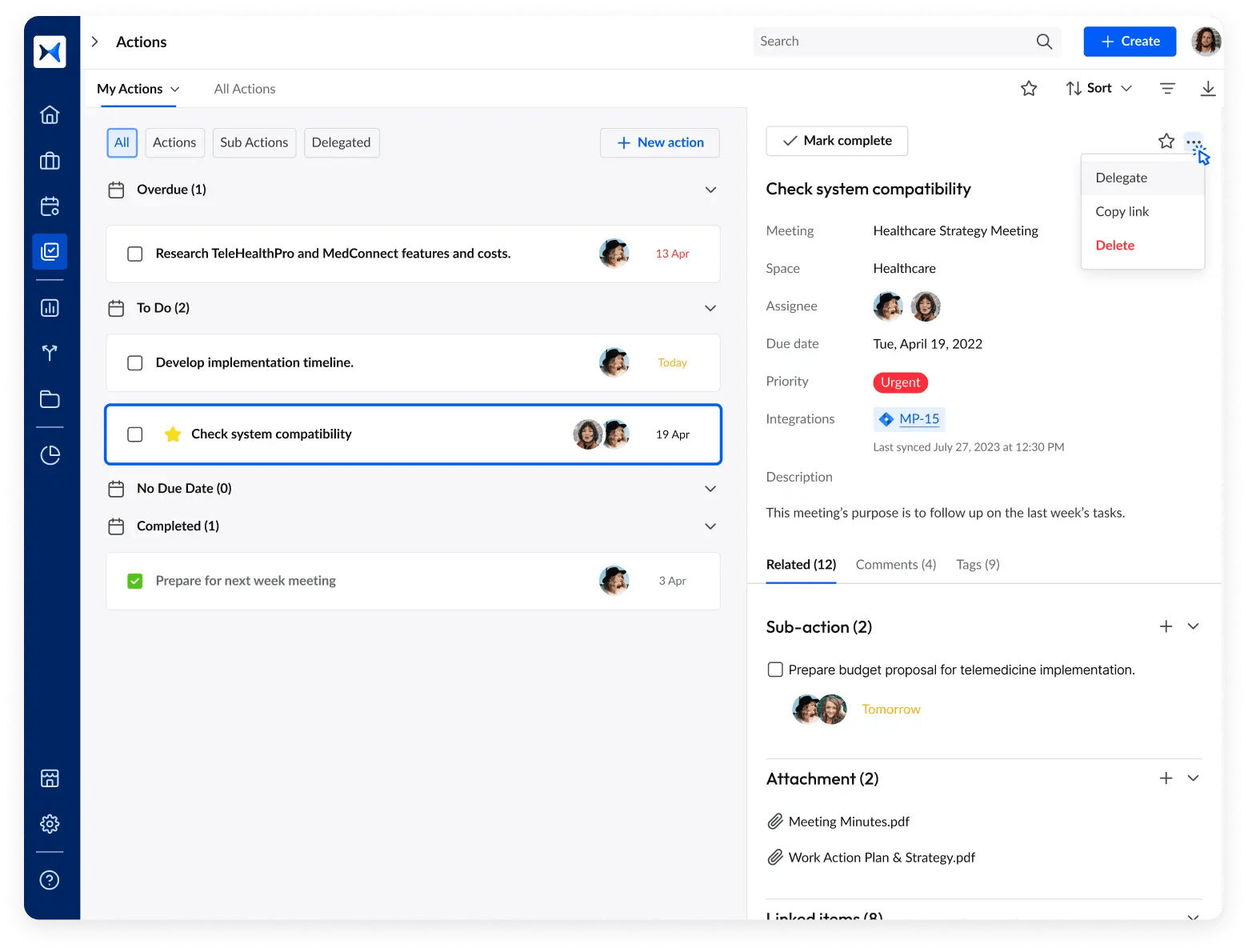
- Action tracking: adam.ai links follow-ups to specific discussions, ensuring that stakeholder feedback is not only acknowledged but also translated into concrete actions. This enhances accountability and stakeholder satisfaction.
- Analytical dashboards: Dashboards provide insights into meeting trends, participation, and task completion rates. These metrics help organizations evaluate meeting effectiveness and stakeholder engagement over time.
Transform how you conduct critical meetings—From meticulous preparation to effective execution and insightful follow-up, adam.ai integrates comprehensive analytics, full customization, and intuitive interfaces with powerful meeting management tools.
Easy onboarding. Enterprise-grade security. 24/7 dedicated support.
The bottom line
NLP enables organizations to understand stakeholder sentiment, fostering more informed and collaborative decision-making. Modern tools like adam.ai empowers teams to analyze emotions, track trends, and create meaningful engagement during meetings.
And while there may be multiple solutions available, here is why adam.ai is the meeting management software platform you can trust:
- adam.ai is one of Atlassian Ventures' portfolio companies.
- In the meeting management software category on G2, adam.ai has been ranked a leader and a high performer for successive quarters in the past years.
- adam.ai has been included in the Forrester Report in the AI-enabled meeting technology landscape.
- adam.ai is trusted and used by powerful teams and organizations worldwide for all types of critical meetings, like board, committee, project management, and business development meetings.
- And most importantly, adam.ai integrates with your existing workflow, is SOC2 compliant, provides dedicated support and success, and has a free trial option.
Subscribe to adam.ai blog
Stay ahead with the latest insights—get our newest blog posts, tips, and updates sent straight to your inbox.