March 3, 2025 · 14 min read
Cybersecurity in the Digital Era: Navigating Risks and Strengthening Enterprise Resilience

Shaimaa Badawi

Cyber threats are an everyday reality for enterprises navigating the digital era. As businesses embrace cloud computing, AI, and remote work, cybercriminals are evolving just as fast, launching sophisticated attacks that disrupt operations, steal sensitive data, and weaken financial stability.
This article explores the biggest cybersecurity risks enterprises face today, how digital transformation has reshaped security challenges, and the role of AI, zero trust, and compliance in safeguarding corporate data.
What are the biggest cybersecurity risks for enterprises today?
Cyber threats are evolving rapidly, and enterprises must stay ahead of risks that can disrupt operations, compromise sensitive data, and erode stakeholder trust. Here are the most pressing cybersecurity risks organizations face today:
1. Ransomware and malware attacks
Cybercriminals use ransomware to encrypt critical business data, demanding payment for its release. Malware, including trojans and spyware, infiltrates systems to steal or corrupt sensitive information. As attacks become more sophisticated, businesses struggle to prevent financial and operational losses.
2. Phishing and social engineering
Hackers manipulate employees into revealing credentials or confidential data through deceptive emails, messages, or phone calls. AI-driven phishing campaigns now craft highly convincing scams, making traditional detection methods less effective.
3. Data breaches and insider threats
Unauthorized access to customer, financial, or proprietary data can lead to legal liabilities, reputational damage, and financial losses. Insider threats, whether malicious or unintentional, are a growing concern, as employees and contractors may compromise security through negligence or misuse.
4. Supply chain and third-party risks
Organizations increasingly rely on third-party vendors, cloud providers, and outsourced services. A security breach at any point in the supply chain can expose enterprises to cyberattacks, as seen in high-profile incidents like the SolarWinds breach.
5. AI-powered cyber threats
While AI enhances security, attackers are also using AI to automate attacks, bypass traditional security measures, and create undetectable malware. This makes threat detection more challenging and increases the speed and volume of attacks.
6. Cloud security gaps
As enterprises shift to cloud-based operations, misconfigured settings, weak access controls, and lack of encryption leave data exposed. Cybercriminals exploit cloud vulnerabilities to gain access to critical systems and sensitive files.
7. Emerging threats in IoT and remote work
The rise of IoT devices and remote work has expanded attack surfaces. Many IoT devices lack built-in security, making them easy targets, while unsecured home networks and personal devices used for work create vulnerabilities.
The digital shift in the oil and gas sector has increased reliance on cloud technologies and IoT devices, making cybersecurity a crucial priority for protecting critical infrastructure.
8. Regulatory and compliance challenges
Enterprises must navigate strict cybersecurity regulations like GDPR, CCPA, and industry-specific frameworks. Failing to comply with security standards can result in legal penalties and reputational harm.
How has digital transformation reshaped cybersecurity challenges?
Digital transformation has revolutionized how enterprises operate, offering efficiency, scalability, and data-driven decision-making. However, this shift has also introduced new cybersecurity challenges that businesses must navigate to stay secure. As enterprises embrace digital transformation in project management, they must also reevaluate their cybersecurity strategies to address new vulnerabilities and risks.
1. Expanded attack surface
With cloud computing, remote work, and IoT adoption, enterprises now operate across multiple networks, devices, and digital platforms. This creates more entry points for cybercriminals, increasing the risk of data breaches and unauthorized access.
2. Cloud security risks
Moving from on-premise data centers to cloud environments has improved flexibility but introduced new vulnerabilities. Misconfigurations, weak access controls, and shared infrastructure can expose sensitive data to cyber threats.
3. AI-powered cyber attacks
As enterprises use AI to automate processes, cybercriminals are leveraging AI to launch sophisticated attacks. AI-driven phishing, deepfake scams, and automated malware make traditional security defenses less effective.
4. Increased regulatory and compliance pressure
Governments and industry regulators have tightened cybersecurity requirements to address digital risks. Enterprises must comply with GDPR, CCPA, ISO 27001, and other regulations, making cybersecurity a critical business priority.
5. Insider threats in a remote workforce
The shift to remote and hybrid work has made insider threats more complex. Employees accessing company systems from unsecured networks or personal devices increase the likelihood of accidental or intentional security breaches.
6. Supply chain and third-party risks
Digital transformation has increased reliance on external vendors, cloud providers, and SaaS platforms. A security failure in any third-party service can compromise an entire organization’s infrastructure.
7. Need for zero trust security models
Traditional perimeter-based security is no longer effective in a digital-first world. Enterprises are adopting zero trust architectures, which verify every access request and limit user privileges to prevent unauthorized access.
How can AI strengthen cybersecurity, and what risks does it introduce?
AI is transforming cybersecurity, making threat detection faster and more efficient. However, its power also comes with risks, as cybercriminals are using AI to launch more sophisticated attacks.
How AI strengthens cybersecurity
- Real-time threat detection and response
AI analyzes vast amounts of data to identify unusual activity, helping security teams detect breaches before they escalate. Implementing AI-driven tools for reducing meeting fatigue with AI can help security teams stay focused and proactive against emerging cyber threats. Machine learning models continuously improve, recognizing new attack patterns in real time. - Predictive analytics for cyber threats
AI can forecast cyber threats by analyzing historical data and identifying patterns. This helps organizations strengthen defenses against emerging attack vectors. Just as NLP for meetings and stakeholder sentiment helps organizations gauge discussions, AI-driven cybersecurity solutions can analyze patterns to detect potential threats. - Automated incident response
AI-driven security systems can contain cyber threats automatically, blocking malicious traffic, isolating compromised accounts, and reducing downtime without human intervention. - Enhanced fraud detection
Financial institutions use AI to detect fraud by identifying anomalies in transaction behavior. AI helps prevent identity theft, phishing scams, and unauthorized access attempts. - Adaptive authentication and access control
AI improves zero trust security by analyzing user behavior and adjusting access permissions dynamically. If an employee’s login activity deviates from their usual patterns, AI can trigger extra verification steps.
Risks AI introduces in cybersecurity
- AI-powered cyber attacks
Hackers are using AI to create advanced phishing scams, automate hacking attempts, and develop malware that adapts to security measures. AI-driven security strategies, similar to the use of machine learning in meeting preparation, can streamline incident response planning by predicting and prioritizing cyber threats. - Bias and false positives
AI models can generate false positives, flagging legitimate activity as malicious. Conversely, false negatives may allow actual threats to go undetected. - Data privacy and security risks
AI systems rely on massive datasets, often containing sensitive information. A breach in AI-driven security platforms could expose critical business and personal data. - Lack of transparency (black box AI)
Some AI-driven cybersecurity tools operate as "black boxes," making it difficult to understand how they make decisions. This lack of transparency can be a challenge when investigating cyber incidents. - Adversarial AI attacks
Cybercriminals manipulate AI models by feeding them misleading data, tricking security systems into ignoring real threats or overreacting to non-existent ones.
Why is zero trust architecture essential for modern enterprises?
Cyber threats have evolved beyond traditional firewalls and perimeter-based security. Zero trust architecture (ZTA) ensures that no one is automatically trusted, inside or outside the organization. Every access request is verified, making it a critical defense strategy in today’s digital landscape.
1. Addresses the weaknesses of traditional security models
Legacy security models assume that users inside a company’s network are trustworthy. But insider threats, compromised credentials, and lateral cyberattacks prove otherwise. Zero trust eliminates this assumption, requiring constant authentication and least-privilege access.
2. Strengthens cloud and remote work security
With remote work and cloud adoption, employees, vendors, and contractors access enterprise systems from multiple devices and locations. Zero trust validates identity, device security, and user behavior before granting access, preventing unauthorized entry.
3. Limits damage from cyber attacks
Even if an attacker gains initial access, zero trust prevents them from moving freely across systems. Micro-segmentation and strict access controls confine threats, minimizing breach impact.
4. Protects against credential theft and phishing
Hackers frequently steal or buy login credentials to infiltrate corporate systems. Zero trust uses multi-factor authentication (MFA), behavior-based authentication, and AI-powered threat detection to verify users even if their credentials are compromised.
5. Enhances compliance with security regulations
Regulations like GDPR, HIPAA, and ISO 27001 require strict data access controls. Zero trust enforces least-privilege policies and continuous monitoring, helping enterprises meet compliance requirements and reduce the risk of legal penalties.
How do cyberattacks impact business operations and financial stability?
Cyberattacks disrupt operations, damage reputation, and create significant financial losses. For enterprises, the consequences can be long-term and difficult to recover from.
1. Operational disruptions and downtime
Cyberattacks like ransomware, distributed denial-of-service (DDoS), and malware can shut down critical business systems, halting operations for hours or even days. Manufacturing plants, hospitals, and financial institutions are especially vulnerable, as downtime directly affects customers and productivity.
The shift from traditional banking to fintech has introduced new cybersecurity concerns, as digital banking platforms and financial technologies become prime targets for cybercriminals.
2. Direct financial losses
- Ransom payments: Many companies pay ransoms to restore encrypted data after an attack, despite security experts advising against it.
- Regulatory fines: Data breaches can trigger heavy fines under GDPR, HIPAA, or other compliance laws.
- Lawsuits and settlements: Customers and partners may sue for damages, leading to legal fees and settlements.
3. Reputational damage and loss of customer trust
A publicized data breach erodes consumer and investor confidence. Customers may leave, vendors may reconsider partnerships, and stock prices can take a hit. Brand reputation can take years to rebuild.
4. Increased cybersecurity and insurance costs
After a breach, businesses must invest heavily in security upgrades, forensic investigations, and crisis management. Organizations that optimize cybersecurity meetings and response strategies can see an improvement in the ROI of reduced meeting time, allowing teams to focus on proactive security measures. Cyber insurance premiums also increase significantly, adding to long-term costs.
5. Supply chain and partner disruptions
A cyberattack on one company can impact an entire supply chain. If a vendor or partner suffers a breach, interconnected systems and shared data could be compromised, leading to widespread disruptions.
What are the key strategies for securing enterprise data and preventing breaches?
Cyber threats are constantly evolving, and enterprises must take proactive steps to safeguard their data. A strong security strategy prevents breaches, protects sensitive information, and ensures business continuity.
1. Implement zero trust architecture
- Assume no one is automatically trusted, whether inside or outside the organization.
- Require continuous authentication for all users and devices.
- Apply least-privilege access, ensuring employees can only access what they need.
2. Strengthen identity and access management (IAM)
- Use multi-factor authentication (MFA) to add extra security layers beyond passwords.
- Implement role-based access controls (RBAC) to limit data exposure.
- Monitor user behavior to detect suspicious activity.
3. Encrypt data at rest and in transit
- Protect sensitive information using end-to-end encryption.
- Secure cloud storage with data masking and tokenization.
- Ensure proper key management policies to control decryption access.
4. Conduct regular security audits and risk assessments
- Identify vulnerabilities with penetration testing and red team exercises.
- Review third-party vendor security to ensure external partners follow best practices.
- Update security policies regularly to adapt to new threats.
5. Deploy AI-driven threat detection
- Use AI-powered security systems to detect anomalies in real-time.
- Automate incident response to contain threats before they spread.
- Continuously train AI models to identify new attack patterns.
6. Secure cloud and endpoint devices
- Configure cloud services with strong access controls and encryption.
- Apply device security policies to prevent unauthorized access from personal or remote devices.
- Use automated patch management to fix software vulnerabilities quickly.
7. Educate employees on cybersecurity best practices
- Train staff to recognize phishing attempts and social engineering attacks.
- Enforce strong password policies and encourage the use of password managers.
- Simulate cyberattacks to improve incident response preparedness. The adoption of AI in meeting management extends beyond corporate discussions, offering enhanced coordination for cybersecurity response teams and crisis handling.
8. Develop a robust incident response plan
- Establish clear roles and escalation procedures for security incidents. Security teams can benefit from structuring incident response discussions with smarter meeting agendas, ensuring that key threats and mitigation strategies are addressed efficiently.
- Maintain secure backups to recover data without paying ransomware demands.
- Regularly test and refine response strategies through simulated cyber drills.
How can organizations ensure compliance with cybersecurity regulations?
Regulatory compliance is a critical part of cybersecurity, protecting sensitive data while helping organizations avoid legal penalties. In highly regulated industries such as healthcare and finance, effective research project management is essential to maintaining cybersecurity compliance while handling sensitive data.
Enterprises must follow industry-specific regulations such as GDPR, HIPAA, ISO 27001, CCPA, and NIST frameworks to meet security standards.
1. Identify relevant compliance requirements
- Determine which regulations apply based on industry and region (e.g., GDPR for data privacy in Europe, HIPAA for healthcare security, and PCI DSS for payment security).
- Stay updated on changing laws and new compliance mandates that may impact operations.
2. Conduct regular security audits and risk assessments
- Perform compliance gap analyses to identify vulnerabilities before regulators do.
- Use third-party security assessments to ensure frameworks are properly implemented.
- Document risk mitigation efforts to demonstrate due diligence in case of audits.
3. Implement strong data protection measures
- Encrypt sensitive data at rest and in transit to prevent unauthorized access.
- Apply access controls and multi-factor authentication (MFA) for identity verification.
- Secure cloud environments with zero trust architecture and strong endpoint protection.
4. Establish clear security policies and procedures
- Develop data handling policies that align with compliance requirements.
- Train employees on cyber hygiene and regulatory responsibilities to reduce human error.
- Maintain detailed incident response plans for quick action in case of a breach.
5. Maintain detailed compliance documentation
- Keep records of security audits, risk assessments, and incident reports.
- Ensure all third-party vendors follow compliance guidelines, as supply chain breaches can lead to regulatory violations.
- Work with legal and compliance teams to align cybersecurity policies with regulatory expectations.
6. Use AI and automation to simplify compliance
- Deploy AI-powered compliance monitoring to detect anomalies in real-time.
- Automate audit log generation and security reporting to track compliance efforts.
- Implement continuous security monitoring to stay ahead of evolving threats. AI-powered meeting tools can also play a role in cybersecurity discussions, helping teams document, track, and analyze security incidents for continuous improvement.
What best practices help build a cybersecurity-aware workplace culture?
Cybersecurity is a company-wide responsibility. A strong security culture ensures that employees, executives, and stakeholders understand risks and actively protect enterprise data.
1. Provide engaging and ongoing cybersecurity training
- Conduct regular security awareness sessions on phishing, social engineering, and password management.
- Use interactive training (simulated attacks, gamification, real-life case studies) to keep employees engaged.
- Tailor training to specific job roles; IT teams need deeper insights than general employees.
2. Enforce strong authentication and access controls
- Require multi-factor authentication (MFA) for all sensitive accounts.
- Use role-based access control (RBAC) to limit user permissions.
- Regularly audit employee access to sensitive data to prevent insider threats.
3. Foster a “report without fear” environment
- Encourage employees to report suspicious emails, behaviors, or security concerns without fear of blame.
- Reward security-conscious behavior through recognition programs.
- Provide a clear and easy process for reporting potential threats.
4. Secure remote work and bring-your-own-device (BYOD) policies
- Require employees to use company-approved devices and secure Wi-Fi connections.
- Implement endpoint security solutions to protect remote access.
- Enforce automatic software updates and patch management.
5. Simulate real-world cyber threats
- Run phishing tests to measure employee awareness and improve response rates.
- Conduct cybersecurity drills so teams know how to handle incidents effectively.
- Test incident response plans regularly to ensure quick action in a breach.
6. Integrate cybersecurity into corporate culture
- Make security part of onboarding and performance evaluations.
- Encourage executive leadership to advocate for cybersecurity best practices.
- Communicate why security matters, not just the rules but the risks and consequences.
How can enterprises strengthen cyber resilience and respond to incidents effectively?
Cyber resilience ensures business continuity, rapid recovery, and minimal disruption when cyber incidents occur. Enterprises need a proactive approach to anticipate, withstand, and recover from cyber threats.
1. Develop and regularly update an incident response plan (IRP)
- Establish clear roles and responsibilities for responding to security incidents.
- Conduct tabletop exercises and simulations to test response readiness.
- Ensure the IRP includes detection, containment, eradication, and recovery steps.
2. Implement AI-powered threat detection and monitoring
- Use real-time monitoring systems to identify anomalies before they escalate.
- Leverage AI-driven security analytics to detect unusual patterns and automate responses.
- Maintain continuous threat intelligence to stay ahead of emerging cyber risks.
3. Strengthen backup and disaster recovery strategies
- Maintain regular, encrypted backups stored securely offline.
- Use the 3-2-1 backup rule: three copies, two different storage types, one offsite backup.
- Test disaster recovery procedures frequently to ensure fast data restoration.
4. Apply a zero trust security framework
- Enforce least-privilege access and require authentication for all users and devices.
- Use network segmentation to contain attacks and prevent lateral movement.
- Continuously verify user identities and endpoint security status.
5. Train employees for rapid threat response
- Provide cybersecurity awareness training to all employees.
- Simulate phishing and social engineering attacks to improve response skills.
- Establish a clear reporting process for suspected breaches.
6. Partner with incident response experts and law enforcement
- Have cybersecurity vendors or response teams on standby for rapid support.
- Collaborate with law enforcement and regulatory bodies when handling major breaches.
- Join threat intelligence sharing networks to learn from industry-wide attacks.
How does adam.ai enhance cybersecurity in enterprise meetings?
adam.ai strengthens cybersecurity in enterprise meetings by ensuring structured, secure, and well-documented discussions that reduce risks and improve decision-making.
- Agenda management: Keep meetings focused on security priorities by structuring discussions around cybersecurity policies, risk assessments, and compliance updates.
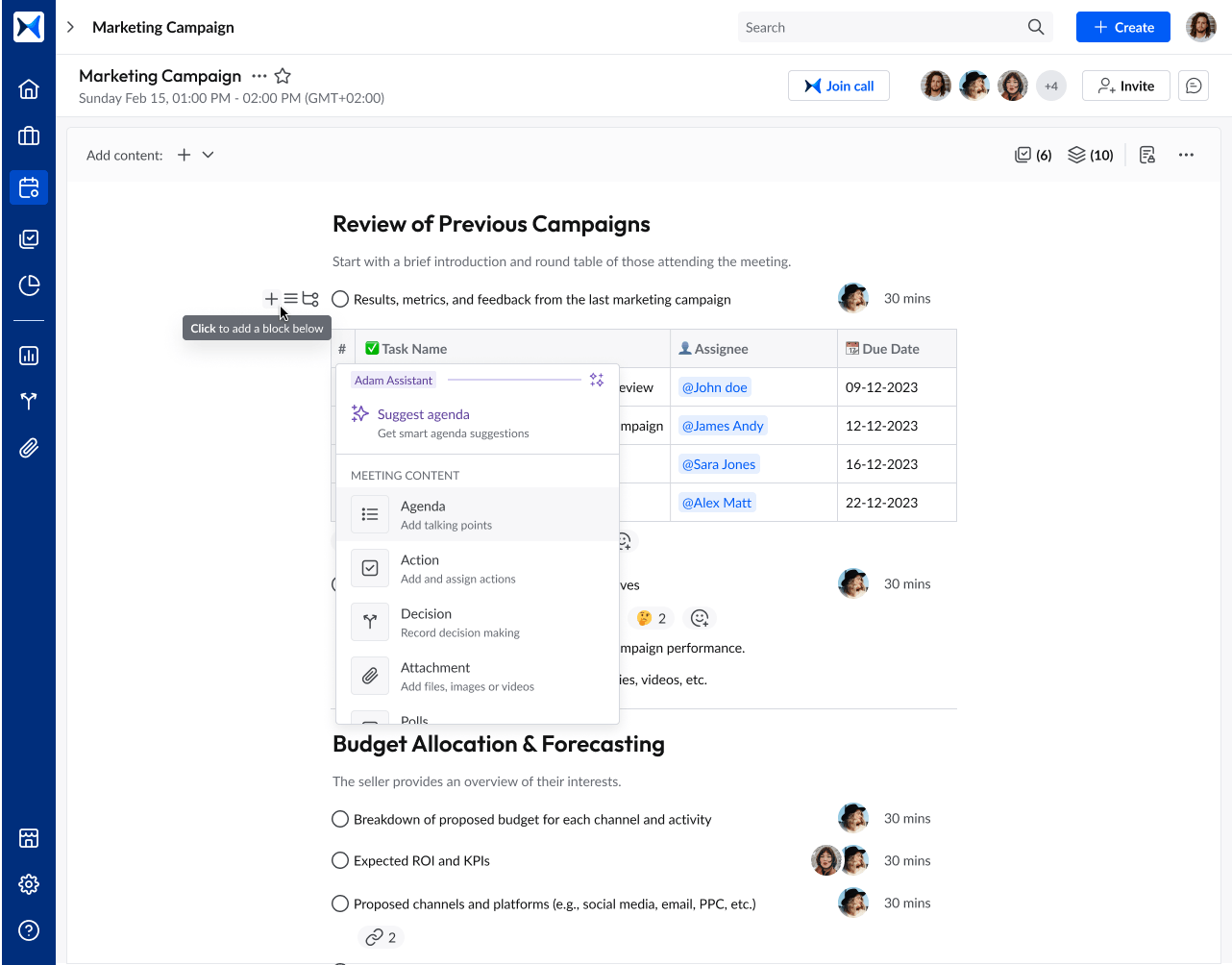
- Content collaboration: Protect sensitive meeting documents by centralizing access, allowing only authorized stakeholders to share and review security-related materials.
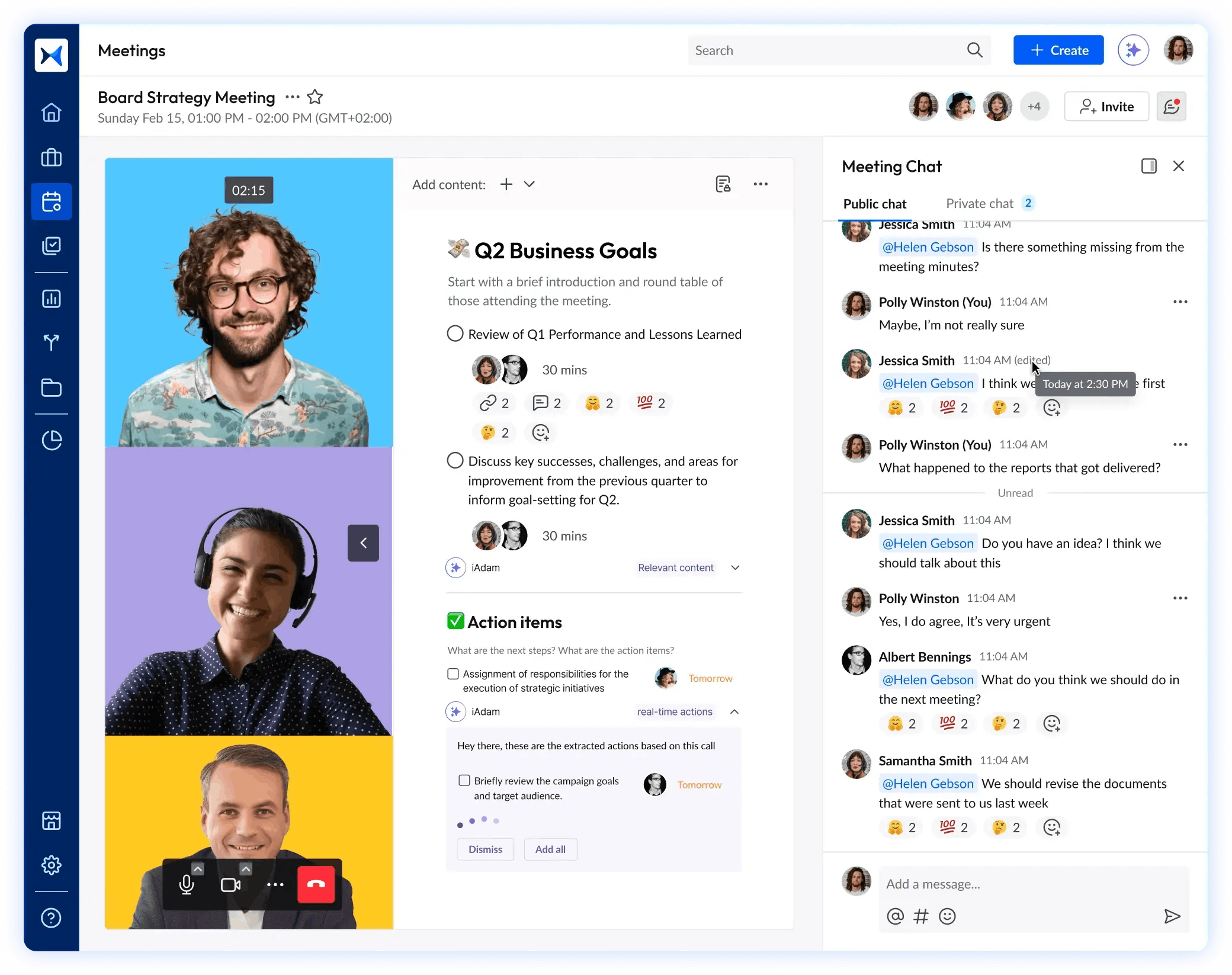
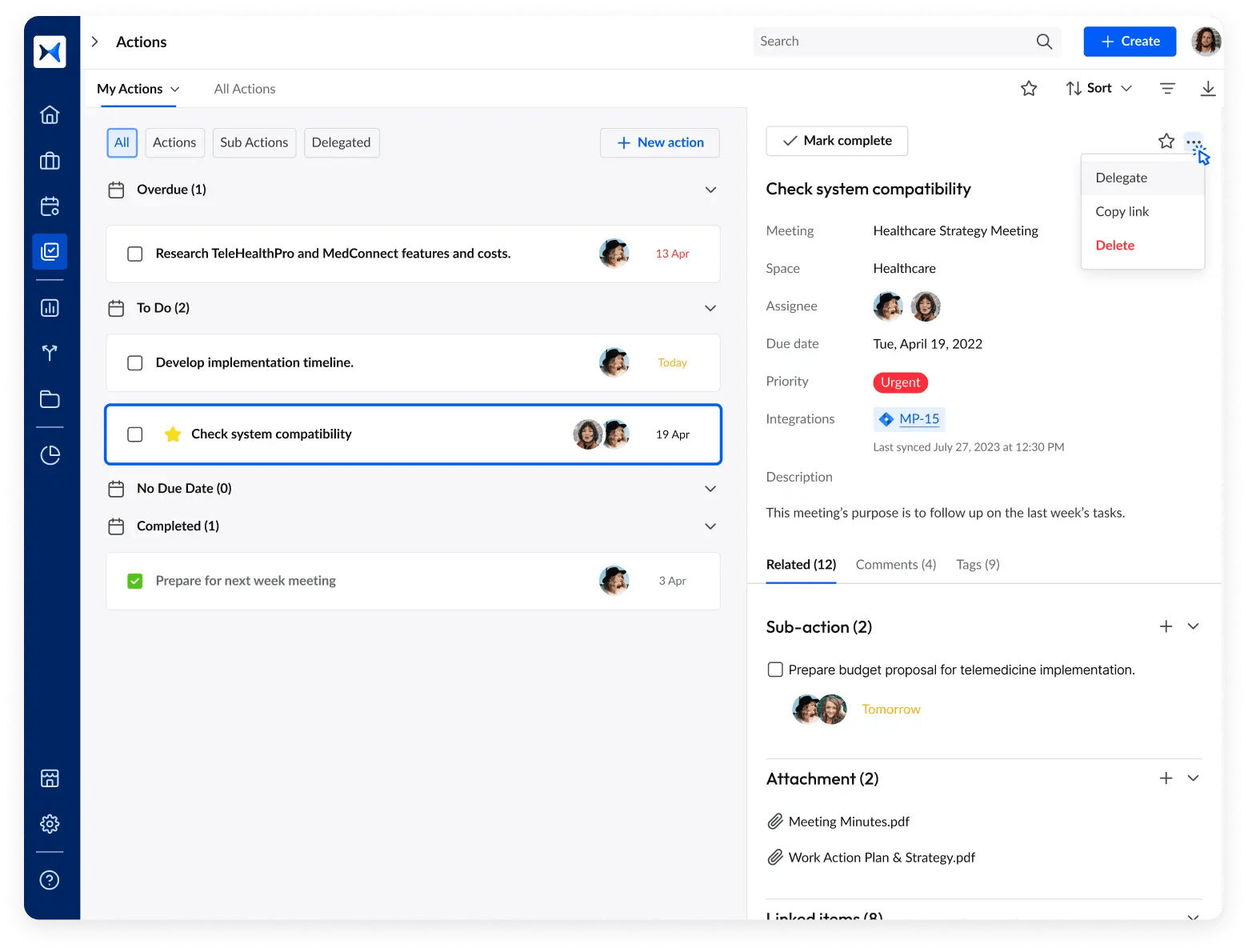
- Action management: Track and assigna security-related tasks, ensuring that cyber risks, compliance actions, and incident response steps are followed through.
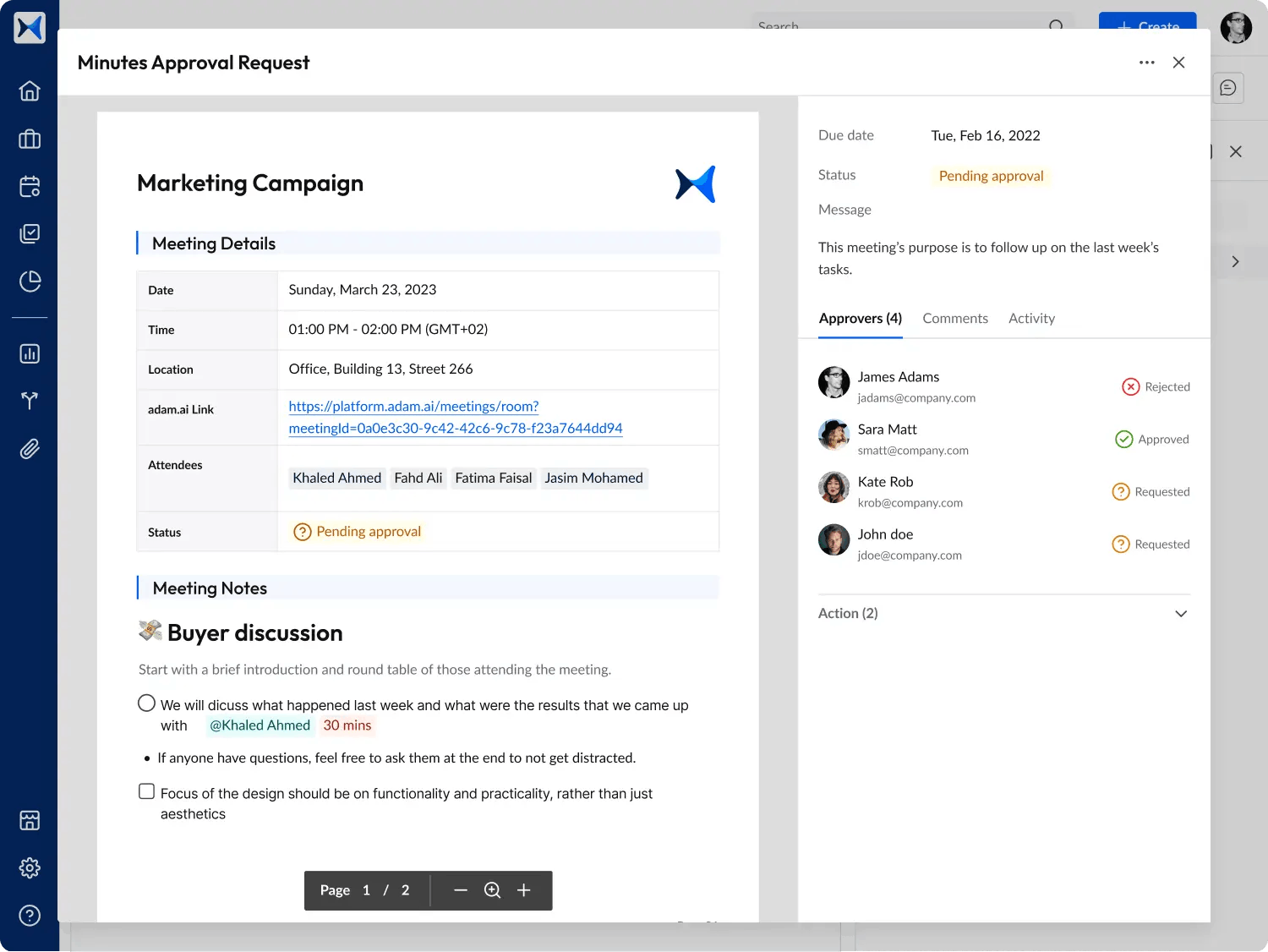
- Meeting minutes: Capture and securely store discussions, providing an auditable record of cybersecurity decisions and risk mitigation strategies.
- Multi-space management: Manage cybersecurity committees separately while ensuring secure access control for different teams handling security operations.
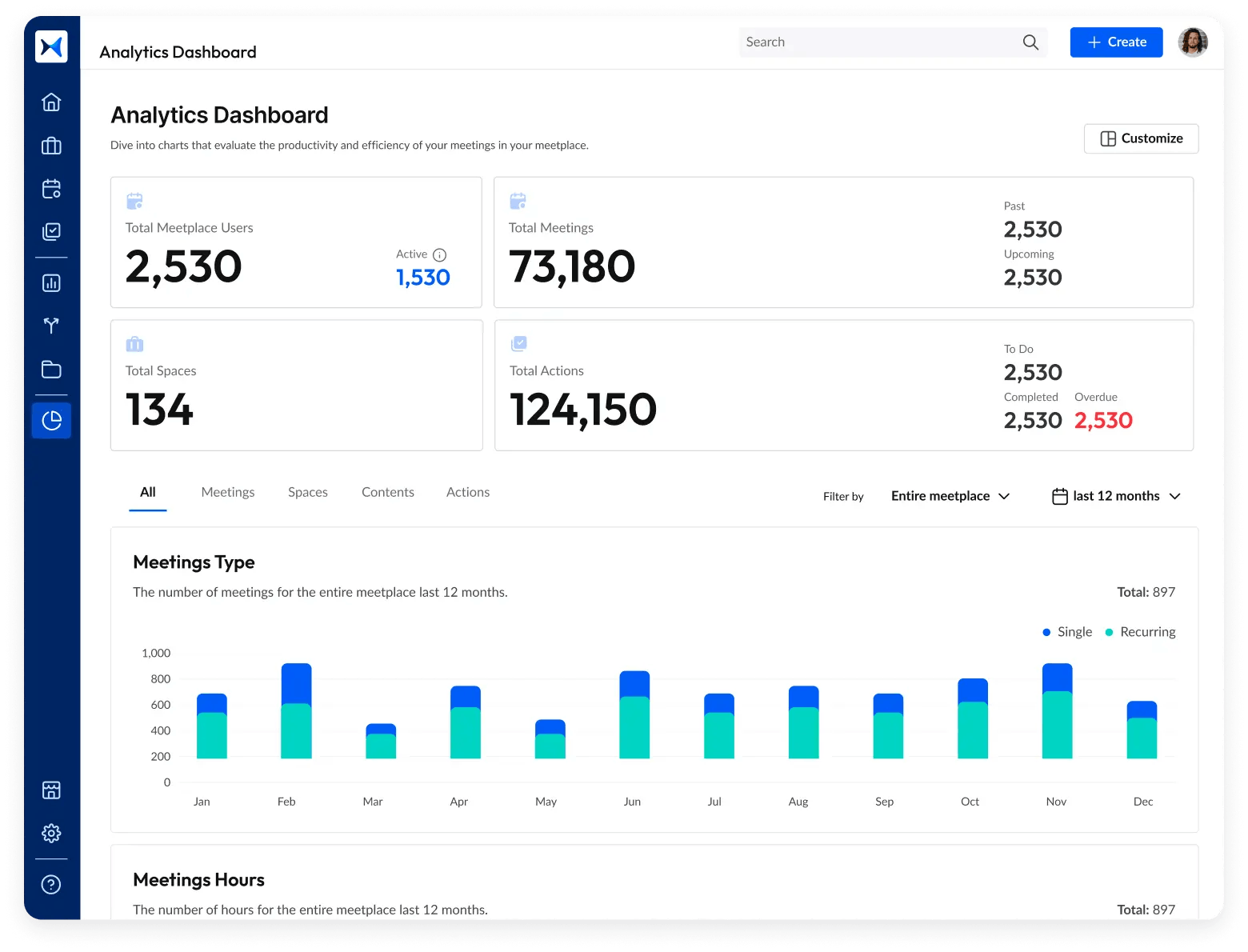
- Analytical dashboard: View meeting outcomes and track progress on security initiatives, unresolved risks, and compliance requirements in real-time.
Transform how you conduct critical meetings—From meticulous preparation to effective execution and insightful follow-up, adam.ai integrates comprehensive analytics, full customization, and intuitive interfaces with powerful meeting management tools.
Easy onboarding. Enterprise-grade security. 24/7 dedicated support.
The bottom line
Cybersecurity is a business-critical function that demands proactive strategies, AI-driven threat detection, and a zero-trust approach. Modern security tools and intelligent platforms now empower organizations to protect data, streamline risk management, and enhance decision-making.
And while there may be multiple solutions available, here is why adam.ai is the meeting management software platform you can trust:
- adam.ai is one of Atlassian Ventures' portfolio companies.
- In the meeting management software category on G2, adam.ai has been ranked a leader and a high performer for successive quarters in the past years.
- adam.ai has been included in the Forrester Report in the AI-enabled meeting technology landscape.
- adam.ai is trusted and used by powerful teams and organizations worldwide for all types of critical meetings, like board, committee, project management, and business development meetings.
- And most importantly, adam.ai integrates with your existing workflow, is SOC2 compliant, provides dedicated support and success, and has a free trial option.
Subscribe to adam.ai blog
Stay ahead with the latest insights—get our newest blog posts, tips, and updates sent straight to your inbox.