November 23, 2023 · 10 min read
Tackling Strategic Risk as a C-Level Executive

Shaimaa Badawi

In the business world, C-level executives face the daunting task of navigating through various challenges, with strategic risk standing out as a crucial element that demands special attention.
Whether it's adapting to market changes, aligning business models with evolving consumer needs, or managing internal operational challenges, understanding strategic risk is key to maintaining a competitive edge.
This article explores the nature of strategic risk and provides tips on how to effectively identify, assess, and mitigate these risks.
What is strategic risk?
Strategic risk is a distinct category of risk that organizations face alongside operational, financial, reputational, and regulatory risks. It pertains specifically to risks that can impede an organization's ability to develop, implement, and execute its main strategic objectives and plans.
In essence, strategic risk encompasses two primary facets:
- Potential impact of strategic decisions: It refers to the risks linked to the choices and decisions made in pursuit of an organization's strategic objectives. These decisions may be flawed, inappropriate, or simply unable to respond effectively to changing market conditions.
- Lack of responsiveness to environmental changes: Strategic risk also encompasses the threat of an organization not adequately adapting to evolving external factors and industry changes that could disrupt or obstruct the achievement of its goals.
Strategic risks can originate from various sources, including but not limited to:
- Acquisitions and mergers: Changes in the competitive landscape, including mergers or acquisitions by competitors, can pose strategic risks.
- Market changes: Shifts in market dynamics, industry trends, or consumer preferences can threaten an organization's strategic plans.
- Financial challenges: Cashflow issues, capital constraints, and cost pressures can hinder strategic initiatives.
- Customer and demand changes: Alterations in customer behavior or demand patterns can affect strategic goals.
- IT and equipment failures: Technological disruptions and equipment failures can disrupt strategic objectives.
- HR inadequacies: Staffing challenges or disruptions in the workforce can impact strategic execution.
Effective management of strategic risk involves not only identifying and assessing these risks but also making informed strategic decisions that account for them, even if they are considered inherent risks that are a part of any business.
What are the types of strategic risk?
Strategic risk types vary from one company to another depending on the industry, consumer base, and a wide range of factors. Here are some of the most common types of strategic risk:
- Regulatory risk: Navigating regulatory risk is essential for organizations, as the introduction of new regulations has the potential to disrupt business operations, introduce new compliance responsibilities, demand technological adaptations, and divert the focus of business leaders.
- Reputational risk: Protecting and preserving an organization's reputation is essential, as it can be at stake due to various factors, including regulatory compliance challenges and shareholder activism.
- Political risk: Political risk poses a substantial concern for businesses, as shifts in political landscapes or governmental policies can lead to disruptions in the supply chain, pricing fluctuations, and changes in market demand.
- Governance risk: Effective governance is a cornerstone of organizational success, but governance risk arises when organizations struggle with weak corporate governance, insufficient oversight, regulatory non-compliance, or ethical lapses among key executives.
- Financial risk: Managing financial risk is crucial, as factors such as market volatility, credit challenges, liquidity constraints, and inadequate financial planning can have a direct impact on an organization's financial health.
- Competitive risk: Remaining competitive in a dynamic market is a constant challenge, as competitive risk emerges when competitors innovate more rapidly or outperform an organization in terms of market share and product or service quality.
- Change risk: Change risk underscores the importance of adapting to evolving circumstances, be it in technology, market trends, or industry standards, to avoid potential disruptions to an organization's strategic objectives.
- Economic risk: Economic risk entails responding to macroeconomic conditions that can affect a company's profitability and investment decisions because of a change in consumer spending habits, disposable income, and market demand.
- Operational risk: Efficient and reliable day-to-day operations are essential for business continuity, but operational risk arises from potential disruptions such as supply chain issues, equipment failures, security breaches, etc.
What is strategic risk management?
Strategic risk management encompasses the process of recognizing, assessing, and proactively addressing risks that could impede an organization's ability to achieve its strategic objectives. It focuses on both internal and external factors that introduce risk into the enterprise, with the ultimate goal of helping the organization succeed in executing its strategic plans.
The key components of strategic risk management involve the following:
- Identification of strategic risks: This involves pinpointing potential risks that may arise, both internally and externally, and that could hinder the organization's strategic goals.
- Strategic risk assessment: Conducting a comprehensive analysis to determine the likelihood of these risks occurring and the potential impact they could have on the organization's strategic objectives.
- Risk mitigation strategy: Developing strategies and approaches to deal with each identified risk, which may include accepting, avoiding, or taking action to eliminate or reduce the risk over time.
- Ongoing monitoring: Continuously monitoring the identified risks to stay informed about any changes, ensuring the organization remains adaptable and responsive to evolving circumstances.
- Documentation and reporting: Thoroughly documenting each stage of the strategic risk management process for future reference and analysis. Reporting is vital to keep key stakeholders, including senior management and the board of directors, informed about risk-related developments.
Depending on the severity and potential consequences of each strategic risk, organizations may choose to accept the risk or take alternative approaches to mitigate or avoid it entirely. Effective strategic risk management empowers leaders to navigate potential obstacles and optimize their performance in pursuit of their strategic goals.
What's the importance of strategic risk management?
Strategic risk management is essential for maintaining an organization's long-term positioning and performance. It requires a deep understanding of the organization's current standing, market sector, target audience, and strategic objectives.
Here are the key reasons why strategic risk management is important:
1. Informed decision-making
In an environment where businesses are constantly exposed to risks, having a robust strategic risk management process allows organizations to make more informed decisions. By identifying and assessing potential risks, companies can weigh the potential benefits against the risks involved, enabling them to make well-considered choices. Whether launching a new business or innovating within an existing market, understanding and managing strategic risks are vital.
2. Mitigating existential threats
History is filled with examples of once-dominant organizations that failed to adapt to changing circumstances and, as a result, faced existential threats. Strategic risk management helps organizations properly evaluate threats and the risks associated with not addressing them. This evaluation can be crucial in preventing existential threats and ensuring the organization's continued relevance.
3. Facilitating innovation
Innovation often involves taking calculated risks. Companies that introduce groundbreaking products or services must navigate a landscape of uncertainty. However, a strong risk management strategy allows organizations to define success, identify potential failure points, assess the associated costs of failure, and formulate responses to overcome obstacles. This empowers businesses to innovate while minimizing the potential negative impacts.
4. Adaptation and competitive advantage
Every successful company embraces a degree of risk, but it's essential to understand and manage those risks effectively. Organizations that excel at managing strategic risks are better equipped to adapt to changing internal and external influences. This adaptability allows them to stay ahead of the competition and seize opportunities that arise.
5. Empowering decision-makers
Strategic risk management empowers leaders at various levels of an organization to make intelligent and well-informed decisions. By comprehending potential dangers, no matter how small, and assessing their potential impacts, leaders can navigate complex business landscapes with confidence.
6. Dynamic and collaborative process
Effective risk management is not a one-time task but a dynamic and ongoing process. It requires continuous evaluation and adaptation as internal and external factors evolve. Additionally, risk management involves collaboration and communication across the entire organization, ensuring that everyone is aligned in their approach to risk.
Strategic risk management is essential for organizations looking to achieve their goals, innovate, adapt to change, and maintain a competitive edge in a constantly evolving business environment. It empowers decision-makers to assess, address, and navigate risks intelligently and collaboratively, ultimately contributing to the long-term success and sustainability of the organization.
Strategic vs. operational risk
Operational risk refers to potential negative consequences arising from interruptions or failures in regular business activities.
These risks can lead to financial losses, affect the organization's reputation, and compromise regulatory compliance. Continual management of operational risk is crucial to mitigate these impacts.
Operational risk includes a wide range of examples like issues in internal processes, system failures, human error, security breaches, and so on.
There's often confusion between strategic risk and operational risk. Understanding operational risk helps in distinguishing the two.
Operational risks are directly connected to the daily functionalities and systems of a business.
In contrast, strategic risk encompasses a broader view, focusing on the future trajectory of an organization. Addressing strategic risk involves considering organizational goals and how they align with decision-making processes. This macro-level approach looks beyond day-to-day operations, focusing on the main strategic objectives.
How to tackle strategic risk in the C-suite
To effectively tackle strategic risk in the C-suite, it's essential to employ a comprehensive and structured approach. Here are the key points to consider for managing strategic risk:
1. Transforming the role of risk managers
- Adopt a comprehensive view of enterprise risk.
- Utilize advanced techniques like data analytics and risk modeling.
- Align capital access with risk management requirements.
- Empower risk managers to make risk management a strategic asset and competitive edge.
2. Ownership and accountability in risk management
- Establish clear ownership of risk at the executive level.
- Identify primary enterprise risk owners.
- Support with performance management and incentives based on key risk metrics.
3. Integrating risk with business operations
- Ensure that risk management is part of every C-suite role.
- Develop an understanding of risk in relation to specific functions.
- Engage in regular, two-way communication with the enterprise risk owner.
4. Alignment on risk prioritization
- Align risk prioritization across the organization.
- Bridge the gap between C-suite risk identification and organization-wide prioritization.
- Avoid resource misallocation and blind spots in risk management.
5. Cultivating a healthy risk culture
- Set a tone for a risk-aware culture within the organization.
- Foster awareness and alignment on risk priorities.
- Implement ongoing training, transparent communication, and strong risk management practices.
6. Understanding different risk types
- Recognize various risk types including internal and external risks.
- Identify positive and negative outcomes associated with strategic risks.
7. Risk assessment
- Conduct thorough assessments to evaluate the magnitude and impact of risks.
- Involve various stakeholders in the assessment process.
- Base risk-taking decisions on these assessments.
8. Establishing a risk management framework
- Outline decision-making processes, policies, and monitoring methods.
- Implement a framework that evaluates changing risk levels.
9. Determining key metrics
- Establish metrics such as economic capital, RAROC, KPIs, and key risk indicators.
- Use these metrics for decision-making, progress tracking, and risk monitoring.
10. Continuous risk monitoring and adaptation
- Regularly monitor and adapt to changes in internal and external risk factors.
- Include regular reporting and trend analysis to fine-tune strategies.
Implementing these structured strategies enables organizations to effectively manage strategic risks, align them with long-term objectives, and ensure sustainable organizational success.
Having explored the various dimensions of managing strategic risk as a C-level executive, one crucial aspect remains: effective communication and decision-making.
In the dynamic environment of the C-suite, where strategic decisions can have far-reaching implications, the need for streamlined, efficient, and productive meetings is crucial.
adam.ai is an all-in-one meeting management platform that empowers C-level executives to enhance the quality and efficiency of their strategic discussions. By integrating this tool into your daily operations, you can expect:
- Structured meeting agendas: Ensure every meeting stays focused on strategic objectives, minimizing deviations and maximizing productivity.
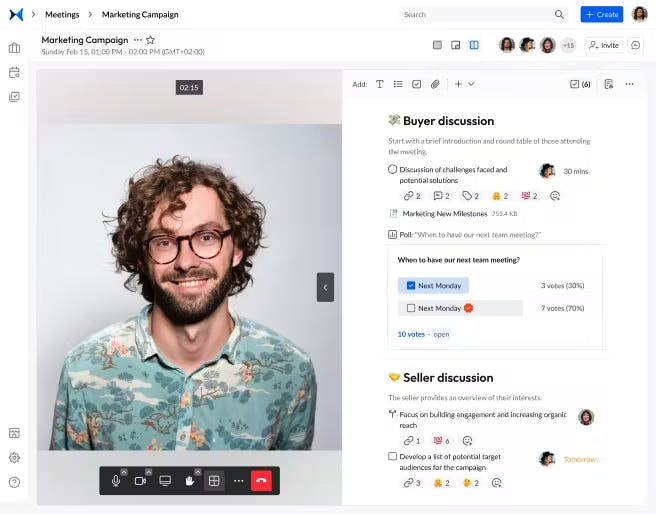
Screenshot from adam.ai: Video call side by side with the meeting content.
- Collaborative decision-making: Facilitate a collaborative environment where insights and risks can be thoroughly discussed, allowing for informed, collective decision-making.

- Real-time data integration: Access critical data and analytics during your discussions, enabling data-driven decision-making that is crucial in managing strategic risks.
- Follow-up and accountability tracking: Monitor the implementation of decisions and accountability, ensuring that strategic plans are executed effectively.
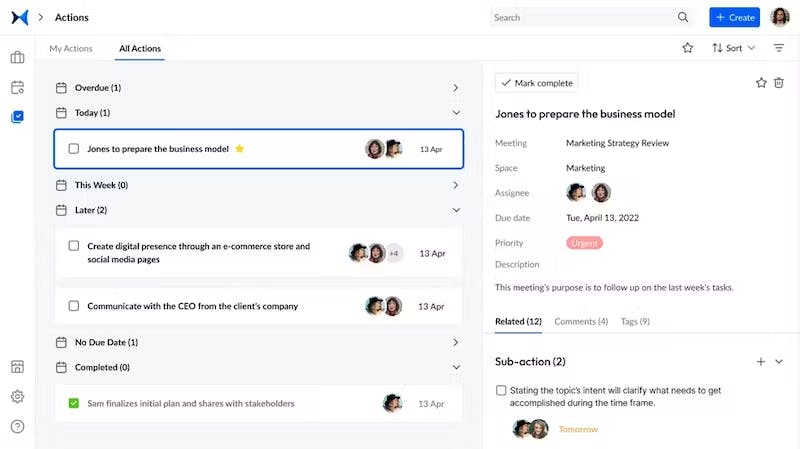
Screenshot from adam.ai: Manage actions.
Get started right now and experience the true meaning of all-in-one meeting management.
Transform how you conduct critical meetings—From meticulous preparation to effective execution and insightful follow-up, adam.ai integrates comprehensive analytics, full customization, and intuitive interfaces with powerful meeting management tools.
Easy onboarding. Enterprise-grade security. 24/7 dedicated support.
The bottom line
Managing strategic risk is not just about averting threats but also about seizing opportunities that drive organizational growth. The strategies and insights discussed here provide a roadmap for C-level executives to understand the complexities of strategic risk and integrate risk management into their leadership approach.
We recommend using an all-in-one meeting management platform, like adam.ai, to facilitate better communication, decision-making, and implementation of strategic initiatives.
And while there may be multiple meeting management solutions available, here is why adam.ai is the all-in-one meeting management platform you can trust:
- adam.ai is one of Atlassian Ventures' portfolio companies.
- In the meeting management software category on G2, adam.ai has been ranked a leader and a high performer for successive quarters in the past years.
- adam.ai has been included in the Forrester Report in the AI-enabled meeting technology landscape.
- adam.ai is trusted and used by powerful teams and organizations worldwide for all types of critical meetings, like board, committee, project management, and business development meetings.
- And most importantly, adam.ai integrates with your existing workflow, is SOC2 compliant, provides dedicated support and success, and has a free trial option.
Subscribe to adam.ai blog
Stay ahead with the latest insights—get our newest blog posts, tips, and updates sent straight to your inbox.