August 6, 2024 · 10 min read
The Corporate Secretary's Role in Shaping Boardroom Success

Shaimaa Badawi

A corporate secretary is the backbone of effective governance and board management, ensuring that every decision is recorded, every action is tracked, and every compliance measure is met. With such a critical role, having the right tools can make all the difference in fulfilling the responsibilities with precision and efficiency. Read on to discover how corporate secretaries can optimize their responsibilities and drive success within the organization.
What is a corporate secretary?
A corporate secretary is a senior officer in a corporation responsible for overseeing administrative operations related to the board of directors and senior management.
This role ensures the company adheres to its governing framework, complies with legal and regulatory requirements, and supports the board by managing meetings and maintaining records. The corporate secretary works closely with c-suite executives to guide governance practices and is one of the key officers essential for the corporation’s setup and ongoing governance.
What is the role of corporate secretary?
A corporate secretary plays a crucial role in the governance and administrative framework of a corporation. This position is essential for ensuring that the board of directors and senior management can operate effectively and in compliance with legal and regulatory requirements.
Key aspects of the role
- Governance advisor: Provides the board with necessary advice and resources to fulfill their fiduciary duties accurately.
- Administrative support: Ensures that board meetings are properly organized and documented, including recording minutes and maintaining company records.
- Link between board and management: Acts as a vital conduit between the board of directors and senior management, facilitating communication and decision-making.
- Promoter of good governance: Develops and implements governance policies and procedures to promote transparency, ethical decision-making, and compliance.
- Regulatory compliance: Maintains a culture of compliance within the organization, ensuring adherence to legal and regulatory standards.
- Key officer: As one of the essential senior officers, the corporate secretary is fundamental to the company’s initial setup and ongoing governance framework.
What are the responsibilities of a corporate secretary?
A corporate secretary holds a critical role in managing various administrative and governance tasks within a corporation. Their responsibilities extend beyond simple clerical duties and involve significant contributions to the company's compliance and governance framework. Here are the key responsibilities of a corporate secretary.
1. Maintaining essential records and documentation
- Ensure all important documents, such as compliance information, stockholder correspondence, stock issues, and proxy statements, are accurately kept and accessible.
- Record minutes during board and committee meetings to reflect the board’s actions and decisions.
2. Supporting board operations and governance
- Provide necessary advice, resources, and guidance to the board, committees, or CEO.
- Set meeting agendas, document meeting minutes, and ensure meetings are properly organized and documented.
3. Developing and sustaining governance frameworks
- Establish and maintain the governance framework, including the board and its committees like finance, audit, compensation, disclosure, and risk management.
- Review and enhance governance programs to keep pace with market changes and best practices.
4. Ensuring legal and regulatory compliance
- Supervise legal entity governance, ensuring adherence to regulatory and statutory requirements, as well as the company’s articles of association and bylaws.
- Administer compliance with the company’s code of conduct and applicable laws, regulations, and industry standards.
5. Facilitating board member development
- Oversee the onboarding process for new directors, ensuring they understand their duties and the company's governance framework.
- Administer board evaluations, governance audits, succession planning, and support directors’ education and training initiatives.
6. Collaborating with executive teams
- Work with directors and executive committees to prioritize discussion subjects and assist in issuing financial press releases, compiling annual reports, and reviewing insurance policies.
- Coordinate activities between board members and senior management to facilitate effective communication and decision-making.
7. Engaging with external service providers
- Liaise with third-party providers such as board portal providers, legal entity management systems, director education resources, and shareholder identification services.
What is another name for a corporate secretary?
The role of a corporate secretary is essential for ensuring effective governance and compliance, and this key position is often known by various titles that reflect its diverse responsibilities, such as the following.
- Board secretary: Often used interchangeably with corporate secretary, emphasizing the role's focus on board-related duties.
- Company secretary: Common in regions like the UK and other Commonwealth countries, highlighting the position's broad scope in corporate governance.
- Chief governance officer: A title that underscores the corporate secretary’s responsibility for governance and regulatory compliance.
- Chief administrative officer: Reflects the administrative and managerial aspects of the role, particularly in larger organizations.
- Corporate board secretary: A variation that emphasizes the connection to the board of directors.
- Head of governance: Frequently used in public or not-for-profit organizations, pointing to the role's governance oversight.
- Corporate secretarial executive/manager: Titles used in some companies to denote a more focused or senior position within the corporate secretarial function.
- Corporate secretarial director: A higher-level title, indicating leadership over the entire corporate secretarial department.
What is the difference between corporate secretary and executive assistant?
The roles of a corporate secretary and an executive assistant, while both crucial in supporting leadership, differ significantly in scope and responsibilities.
Scope of responsibilities
- Corporate secretary: Focuses on governance, compliance, and board-related tasks. This includes managing board meetings, maintaining corporate records, and ensuring the organization adheres to legal and regulatory requirements.
- Executive assistant: Provides direct support to executives by managing schedules, emails, and administrative tasks. An executive assistant often acts as a gatekeeper and may handle more strategic tasks like prioritizing communications, managing projects, and making decisions on behalf of the executive.
Decision-making authority
- Corporate secretary: Plays a vital role in the organization’s governance structure but typically does not make high-level decisions independently. Their work involves ensuring that decisions made by the board and executives comply with legal and regulatory standards.
- Executive assistant: Often has the authority to make decisions that facilitate the executive's workflow, such as scheduling priorities, delegating tasks, and handling sensitive communications. The role requires a high level of initiative and the ability to anticipate the executive’s needs.
Educational and professional requirements
- Corporate secretary: Usually requires specialized knowledge in corporate law, governance, and compliance. This role often demands qualifications such as a law degree, certification in corporate governance, or membership in professional bodies.
- Executive assistant: Typically requires a broad skill set in administration, project management, and communication. While a university degree is often preferred, experience and proven ability to handle complex tasks with minimal oversight are highly valued.
Impact on the organization
- Corporate secretary: Integral to the organization’s legal and ethical standing, ensuring that the company operates within the framework of the law and adheres to corporate governance best practices.
- Executive assistant: Directly impacts the productivity and effectiveness of executives by managing day-to-day operations, allowing leaders to focus on strategic decisions. The role can evolve into a strategic partner for the executive, contributing to decision-making processes and organizational success.
Is a company secretary a director?
While there are overlaps between the roles of a company secretary and a director, they are fundamentally distinct positions within a company.
Role and responsibilities
- Director: Holds ultimate responsibility for the management of the company and its compliance with all relevant laws. Directors are legally accountable for the company’s actions and decisions.
- Company secretary: Assists the directors by managing administrative tasks and ensuring corporate compliance. The secretary’s role is supportive, helping to alleviate the directors’ administrative burden but not holding the same level of legal responsibility.
Legal accountability
- Director: Legally accountable for all aspects of the company’s operations and decisions. This includes ensuring the company adheres to corporate laws and governance practices.
- Company secretary: Although the secretary plays a key role in advising on compliance and corporate governance, the legal responsibility for compliance remains with the directors.
Appointment and necessity
- Director: Required for all companies; they are the primary decision-makers and leaders.
- Company secretary: Not legally required for private limited companies, but highly recommended, especially for large proprietary or public companies, to ensure compliance and manage administrative functions.
Dual roles
A company secretary can also be a director but cannot simultaneously serve as the company’s auditor or be an undischarged bankrupt without court permission. When a company secretary is also a director, they take on the legal responsibilities associated with directorship in addition to their secretarial duties.
What qualifications are needed to become a corporate secretary?
Becoming a corporate secretary requires a blend of specialized knowledge, skills, and personal attributes. This role has evolved into a senior position within organizations, demanding a deep understanding of corporate law, governance, and regulatory compliance. Here are the key qualifications and skills needed to excel as a corporate secretary.
Educational background
A degree in law, business administration, or a related field is often preferred. Many corporate secretaries are lawyers or business professionals with governance expertise. Extensive training in corporate governance is crucial, as the role requires staying up-to-date with evolving laws and regulations.
Professional certifications
Holding certifications such as the Institute of Chartered Secretaries and Administrators (ICSA) qualification or membership in relevant professional organizations can be highly beneficial. In some jurisdictions, specific licenses or certifications may be required to serve as a corporate secretary, adding credibility and demonstrating a commitment to ethical standards.
Key skills
- Legal knowledge: A thorough understanding of corporate governance principles, local and international laws, and regulatory requirements is essential. Corporate secretaries must ensure that the company complies with legal standards and manages legal risks effectively.
- Organizational skills: The ability to manage multiple responsibilities, such as record keeping, coordinating board meetings, and facilitating communication, is vital. Strong time-management skills are also necessary to meet deadlines and adapt to changing priorities.
- Communication skills: As the liaison between the board of directors, senior management, and other stakeholders, corporate secretaries must excel in both verbal and written communication. They need to convey complex information clearly and maintain confidentiality.
- Critical thinking and problem-solving: Corporate secretaries must be resourceful problem-solvers, capable of developing and implementing solutions within the framework of the law and company policies.
- Integrity and ethical standards: Handling sensitive information and advising on corporate governance requires the highest ethical standards. Corporate secretaries must build trust with stakeholders and act in the best interests of the organization.
Personal attributes
Being detail-oriented, organized, and a skilled multitasker is essential for managing the diverse responsibilities of the role. Strong relationship-building skills and the ability to act as a mediator between different parties within the organization are also critical.
Empowering corporate secretaries with adam.ai
Corporate secretaries play a pivotal role in ensuring effective governance, compliance, and efficient decision-making. With adam.ai, an intelligent meeting management platform designed for boards, committees, and projects, corporate secretaries can leverage a powerful suite of tools to streamline their responsibilities and enhance their overall impact.
Explore how adam.ai can empower corporate secretaries with the following features:
- Real-time content collaboration: Streamline the preparation and management of board and committee meetings with adam.ai’s smart note-taking system. Record agenda items, actions, decisions, votes, and notes in a clear, organized manner, ensuring that all meeting documentation is accurate and accessible.
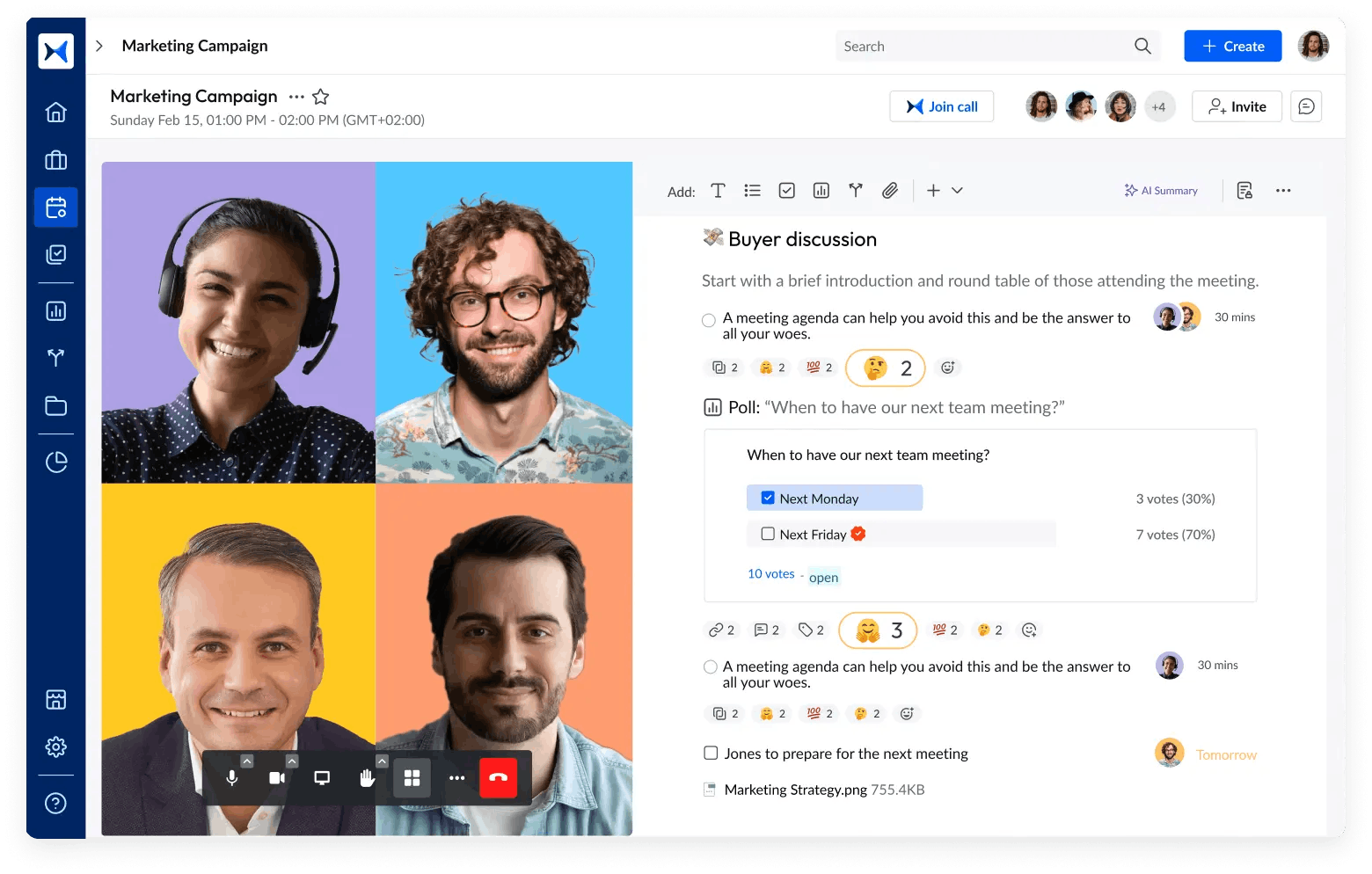
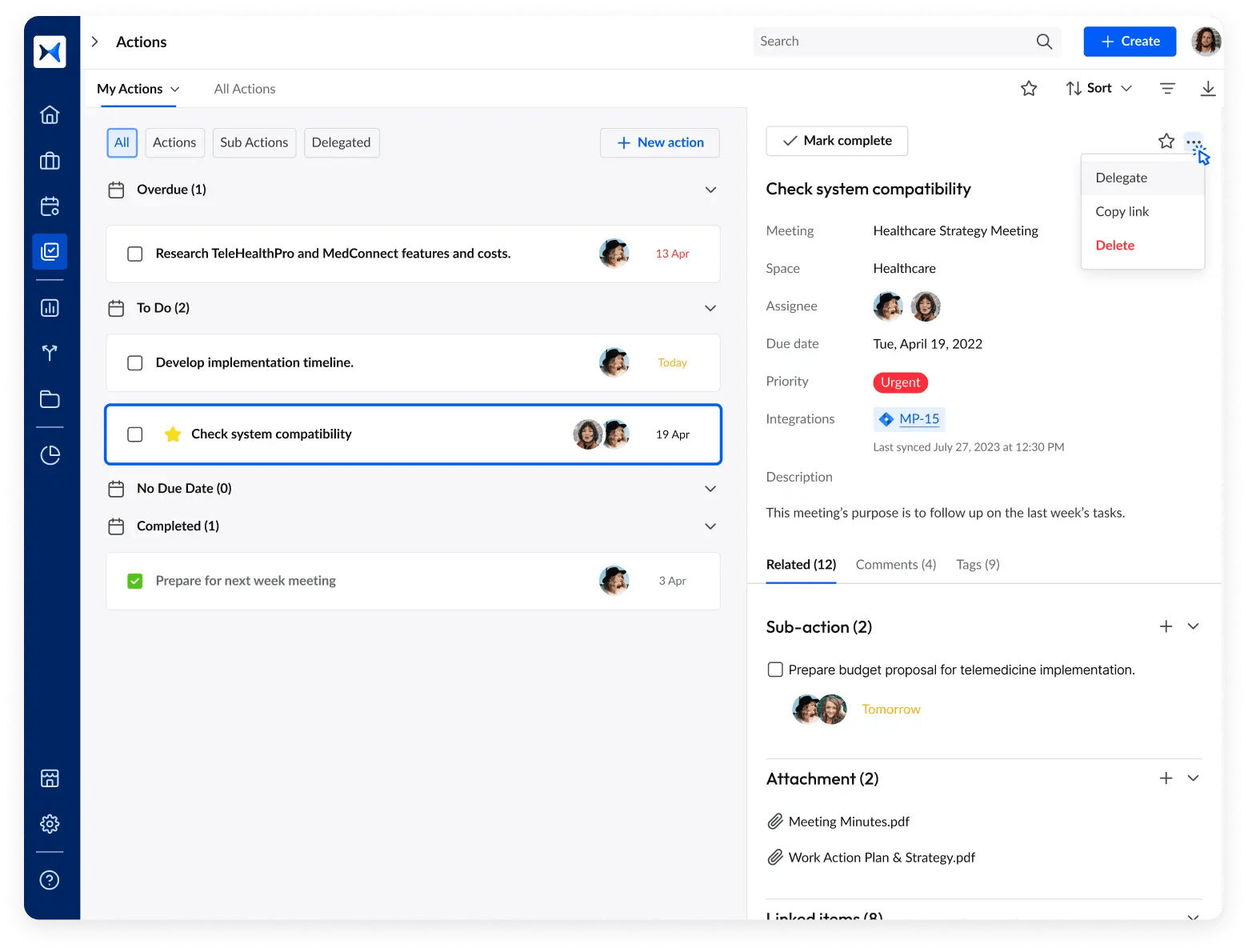
- Action and decision tracking: Ensure accountability and follow-through on board decisions by using adam.ai’s action and decision tracking features. Corporate secretaries can monitor progress, set reminders, and keep track of all tasks assigned during meetings, ensuring nothing slips through the cracks.
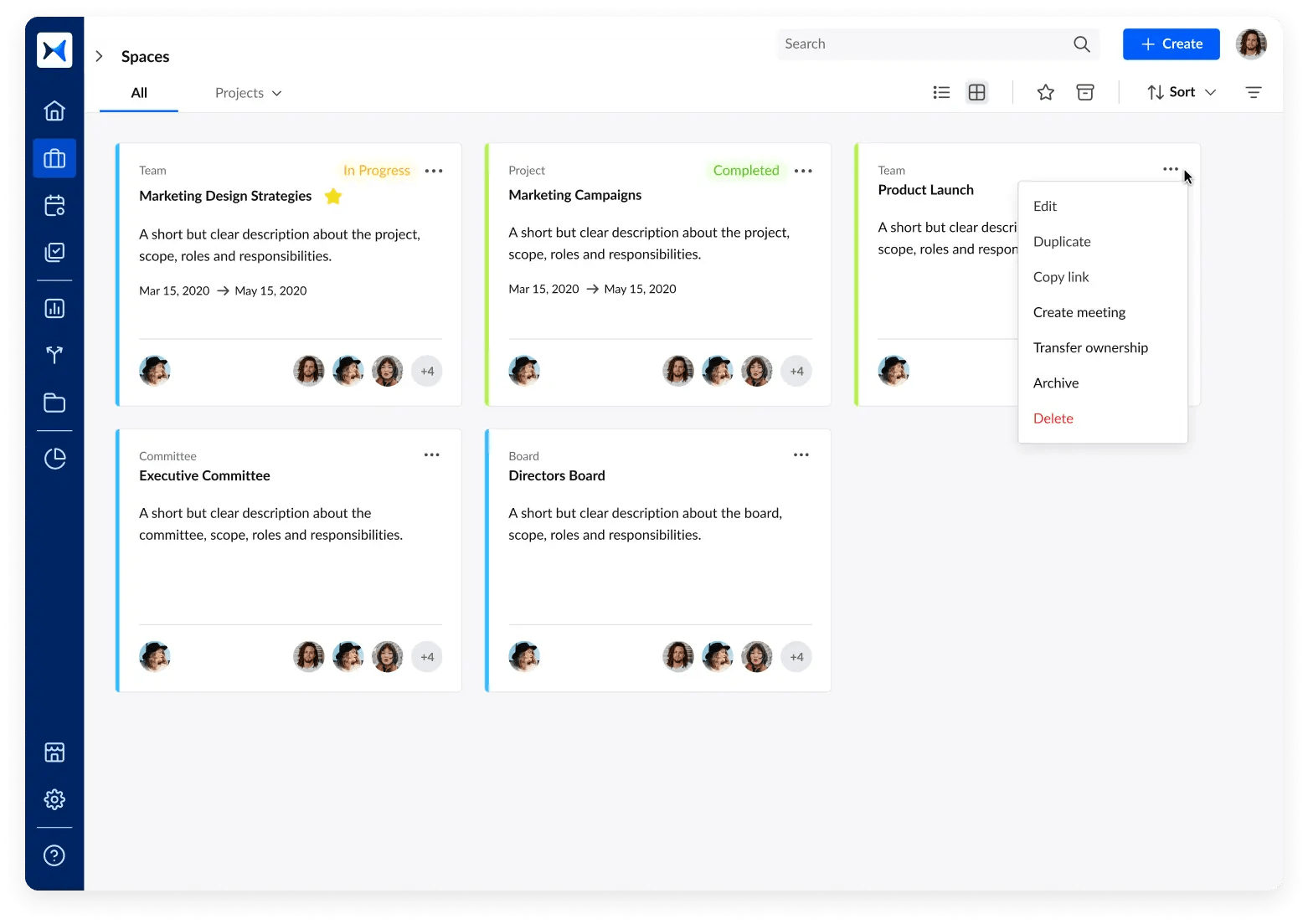
- Multi-space management for meetings and boards: Organize meetings into dedicated spaces for different committees, teams, and projects. This feature helps corporate secretaries maintain detailed records, streamline communication, and manage the governance of various entities within the organization efficiently.
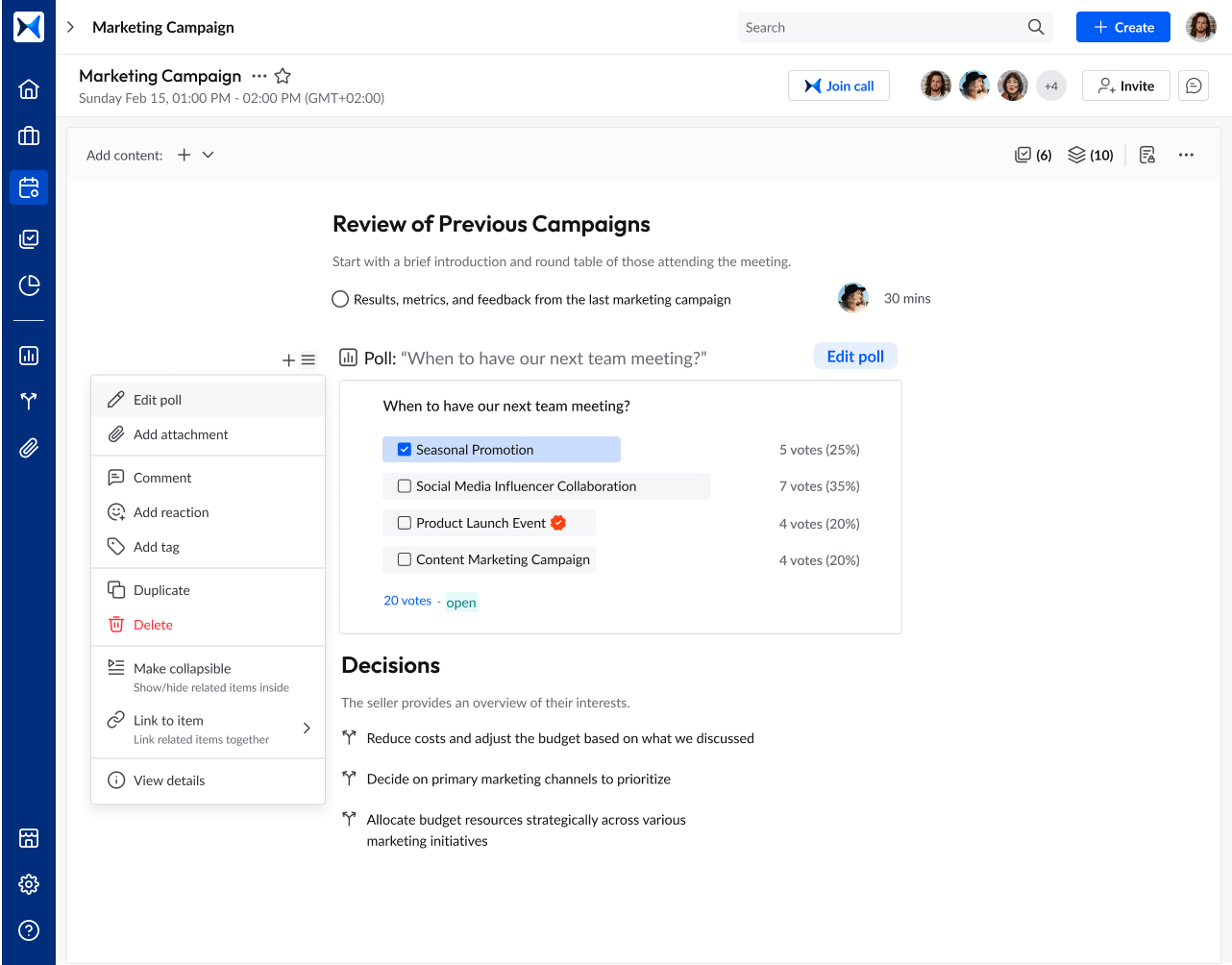
- Voting and decision management: Simplify the voting process by conducting polls within the platform, attaching relevant documents, and recording all decisions made during meetings. adam.ai ensures that every vote is documented, with clear records of who voted and how, which is crucial for compliance and transparency.
- Automated meeting minutes: Save time and ensure accuracy by automatically generating and sharing meeting minutes. adam.ai supports the documentation of discussions and decisions, making it easier for corporate secretaries to distribute minutes promptly and keep all stakeholders informed.
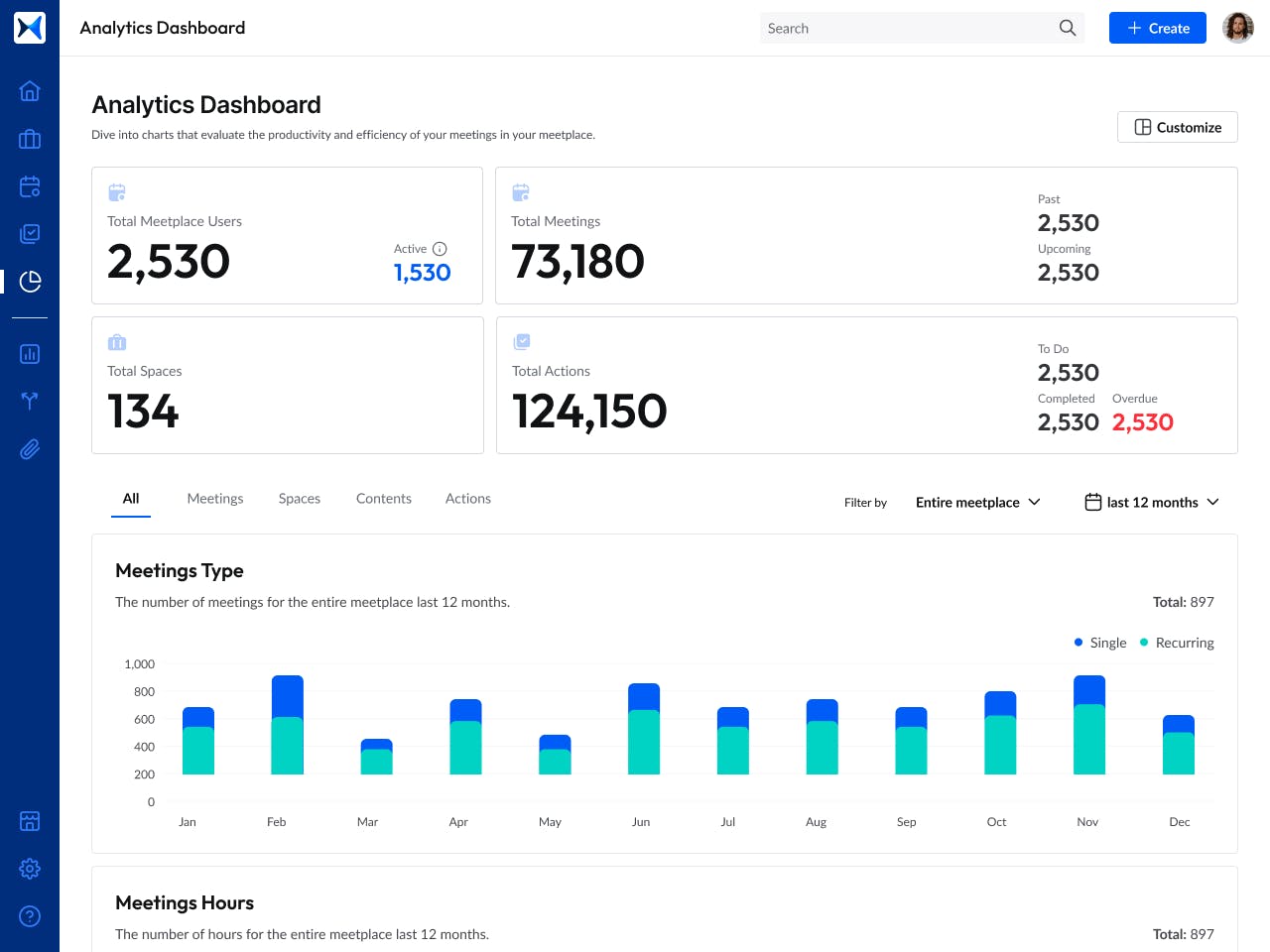
- Analytics dashboard: Leverage insights from the analytics dashboard to assess meeting participation, track decision outcomes, and monitor the progress of action items. This tool helps corporate secretaries manage the effectiveness of board activities and supports informed decision-making.
Transform how you conduct critical meetings—From meticulous preparation to effective execution and insightful follow-up, adam.ai integrates comprehensive analytics, full customization, and intuitive interfaces with powerful meeting management tools.
Easy onboarding. Enterprise-grade security. 24/7 dedicated support.
The bottom line
By leveraging modern tools designed specifically for the demanding role of a corporate secretary, you can elevate your impact on the organization, streamline your workflow, and ensure that every aspect of governance and compliance is handled with the utmost care and attention to detail.
And while there may be multiple solutions available, here is why adam.ai is the meeting management software platform you can trust:
- adam.ai is one of Atlassian Ventures' portfolio companies.
- In the meeting management software category on G2, adam.ai has been ranked a leader and a high performer for successive quarters in the past years.
- adam.ai has been included in the Forrester Report in the AI-enabled meeting technology landscape.
- adam.ai is trusted and used by powerful teams and organizations worldwide for all types of critical meetings, like board, committee, project management, and business development meetings.
- And most importantly, adam.ai integrates with your existing workflow, is SOC2 compliant, provides dedicated support and success, and has a free trial option.
Subscribe to adam.ai blog
Stay ahead with the latest insights—get our newest blog posts, tips, and updates sent straight to your inbox.