June 24, 2024 · 10 min read
Simplifying Your Corporate Resolution: An Informative Step-by-Step Approach

Shaimaa Badawi

Navigating the corporate resolution process can often feel like an uphill battle, but it's essential for ensuring effective governance and making well-informed decisions. Embracing innovative solutions and streamlining procedures can significantly enhance resolution management, making it more efficient and transparent. This article explores various features and strategies that can optimize the corporate resolution process, helping your organization run more smoothly and effectively.
What is a company's corporate resolution?
A corporate resolution is a formal document created by a company's board of directors to officially record significant decisions and actions taken on behalf of the corporation. This document outlines specific resolutions, such as the approval of contracts, the sale of assets, or other key business transactions. It serves as a legal record, ensuring transparency, accountability, and compliance with state regulations. Corporate resolutions help demonstrate the independence of the corporation from its shareholders, providing a clear, documented trail of decisions that are often required for legal and financial purposes.
What are the types of corporate resolutions?
Corporate resolutions document the actions and decisions made by a company's board of directors and, sometimes, its shareholders. Here are the main types of corporate resolutions:
1. Board resolutions
These are decisions made by the board of directors and often involve significant operational and strategic actions. Common types include the following examples:
- Opening financial accounts: Authorizing the opening of bank accounts or obtaining credit cards.
- Contractual agreements: Entering into contracts with third parties.
- Property transactions: Purchasing or selling company-owned real estate.
- Leasing agreements: Approving leases for equipment or facilities.
- Executive appointments: Hiring executive-level employees or voting in new board members.
- Intellectual property: Adopting new trademarks or developing corporate logos.
- Financial decisions: Securing loans or approving the sale of shares.
- Administrative changes: Changing the registered address or appointing audit committees.
2. Shareholder resolutions
These resolutions are made by the shareholders during annual meetings or special meetings and typically involve major corporate changes. Examples include the following:
- Auditor appointments: Appointing or exempting an auditor.
- Financial approvals: Approving annual financial statements.
- Director elections: Electing or re-electing directors.
- Major changes: Approving changes to the company name or constitution.
3. Special resolutions
These require a higher level of approval, usually at least 75% of the shareholder votes. They are used for significant changes or decisions, such as the following examples:
- Constitutional changes: Altering any provisions in the company constitution.
- Share allocations: Allotting new shares.
- Company name changes: Changing the company’s registered name.
4. Ordinary resolutions
These require a simple majority (more than 50%) of votes to pass. They are used for more routine decisions, such as the following:
- Director removal: Removing a director before the end of their term.
- Director appointments: Appointing or re-appointing directors, including those over a certain age.
What is the difference between a corporate resolution and minutes?
Understanding the distinction between corporate resolutions and meeting minutes is crucial for maintaining proper board governance and legal compliance within a corporation. Here are the key differences:
Purpose and content
Corporate resolution
- A corporate resolution is a formal document that records a specific decision made by the board of directors.
- It includes detailed descriptions of the action authorized, such as approving contracts, selling assets, or making significant policy changes.
- The resolution is legally binding and provides a clear directive for specific actions to be undertaken by the corporation.
Meeting minutes
- Meeting minutes are a comprehensive record of everything that transpires during a meeting, including discussions, decisions, and other notable activities.
- They document all proposals, whether accepted or rejected, and include details like the time, date, attendees, and agenda items discussed.
- Minutes ensure there is a thorough record of the meeting proceedings for future reference and accountability.
Scope of documentation
Corporate Resolution:
- Focuses solely on specific decisions or actions that the board has agreed upon.
- Serves as an official record of authorization for particular corporate activities.
Meeting minutes
- Encompass a broader scope, capturing the overall flow of the meeting, including all deliberations, decisions, and interactions.
- Provide context and background for each decision made, not just the decisions themselves.
Legal requirements and compliance
Corporate resolution
- Required for formalizing major corporate actions and ensuring they are legally binding.
- Often necessary for regulatory compliance, demonstrating that the corporation is acting independently of its shareholders.
Meeting minutes
- Required for maintaining a formal record of board meetings, which is often a legal requirement for incorporated entities.
- Ensure transparency and accountability by providing a detailed account of the board's activities.
Structure and format
Corporate resolution
- Typically concise, focusing on the specific action being authorized.
- Form and structure can vary, but it is generally a straightforward document outlining the decision and any relevant details.
Meeting minutes
- More detailed and structured, including a comprehensive account of the meeting.
- Often formatted to include standard sections like attendee lists, agenda items, resolutions proposed and their outcomes, and other relevant discussions.
Usage and frequency
Corporate resolution
- Used when a specific decision needs to be formally documented and authorized by the board.
- May be created independently or as part of the meeting minutes if the resolution is passed during a meeting.
Meeting minutes
- Created for every board meeting, capturing all activities and decisions during the meeting.
- Serve as a continuous record of the board's governance and oversight activities.
Do I need minutes or a resolution?
Minutes are needed to document the proceedings of a formal meeting where decisions are made. A resolution is required to record a formal decision, whether made during a meeting or through a written process without holding a meeting. The company's constitution should be consulted to determine if written resolutions are permissible for the specific decision.
Who signs a written resolution?
Understanding who signs a written resolution is crucial for ensuring that the process is legally compliant and correctly executed. Here's a comprehensive breakdown:
1. Shareholder agreement
- Each shareholder typically signifies agreement by signing and returning the written resolution to the company. This can be done either on paper or electronically.
- A shareholder’s agreement is considered valid when the company receives an authentic document that (a) identifies the specific resolution and (b) clearly indicates the shareholder’s agreement to the resolution.
- Agreement can be indicated via email response or actions performed on a website, provided that the company's policies allow such methods.
2. Voting process
- Shareholders vote on proposed resolutions by signing and returning the written resolution to the company.
- For a vote to be valid, the company must receive the signed written resolution before the lapse date, which is typically set by the company's internal policies.
- Shareholders not wishing to vote in favor simply do not sign or return the written resolution.
3. Finalizing and signing the document
- Corporate resolutions must comply with applicable laws and include all necessary legal components. Consulting with a qualified attorney can help ensure the resolution is legally compliant.
- Once finalized, the resolution must be signed by the person who brought the decision to the board or the individual charged with enacting it. This is typically a board member or the corporate secretary.
Can a resolution be passed without a meeting?
Yes, a resolution can be passed without a formal meeting. Here’s how it works:
Two methods of passing resolutions
- Formal meetings: Traditionally, resolutions are passed during formal meetings where shareholders or board members convene to discuss and vote on proposed resolutions.
- Written resolutions: Resolutions can also be passed in writing, without holding an actual meeting. This method is often used when it is impractical for directors or shareholders to meet in person but a decision still needs to be made.
Procedural requirements
- Statutory compliance: Whether a resolution is passed in a meeting or in writing, it must comply with statutory requirements to be valid. These requirements ensure the resolution is enforceable and not void or voidable.
- Contractual agreements: Companies may also have contractual obligations that dictate how resolutions should be passed. It’s essential to adhere to these agreements to avoid disputes or legal issues.
Circulating resolutions
- Definition: A circulating resolution is a written resolution that is circulated among the shareholders or board members for approval without the need for a formal meeting.
- Approval process: To pass a circulating resolution, the document outlining the resolution is distributed to all relevant parties. Each party reviews and signs the document to indicate their agreement.
- Practical use: This method is particularly useful when swift decisions are needed or when gathering all shareholders or directors for a meeting is not feasible.
Ensuring validity
- Documentation: It’s crucial to document the process meticulously, ensuring that the resolution clearly identifies the decision being made and that all necessary signatures are obtained.
- Legal compliance: Consulting with legal professionals can help ensure that the written resolution meets all legal requirements and is enforceable.
How to write a company resolution
Creating a company resolution involves several clear steps to ensure it is legally binding and properly documented. Here is a concise guide on how to write a company resolution:
1. Title and identification
- Company name: Start by writing the name of the company at the top of the document.
- Governing body: Identify the governing body making the decision, such as the board of directors.
- Resolution number: Assign a unique resolution number to differentiate it from other resolutions.
2. Date and location
- Meeting date: Indicate the date when the resolution is being drafted or passed.
- Location: Specify the location where the decision is made, if applicable.
- Time: Include the time of the meeting or decision-making process.
3. Resolution title
- Title: Create a concise title that reflects the intent of the resolution. For example, “Resolution to approve annual budget.”
4. Preamble statements
- Purpose: Begin with statements that provide context and reasons for the resolution. Each statement should start with "whereas." Example: “Whereas, the company requires a new Chief Financial Officer to manage financial operations...”
5. Resolution statements
- Action clauses: Clearly state the actions to be taken. Each action statement should begin with "resolved." Example: “Resolved, that the company will hire a new Chief Financial Officer.”
6. Voting and approval
- Voting record: Include a section to record the votes of the board members. List each member’s name and their vote (yes or no). Example: “John Smith - Yes, Jane Doe - No.”
- Approval signature: Provide space for the board president or chairperson to sign and date the document. Optionally, include spaces for other officers to sign.
7. Finalization
- Documentation: Ensure all necessary signatures are obtained and the document is dated.
- Storage: Store the signed resolution securely, either in physical files or using digital board management software for easy access and organization.
Achieve seamless resolutions with adam.ai
Streamlining the corporate resolution process is essential for effective governance and swift decision-making. adam.ai, the intelligent meeting management platform for boards, committees, and projects, offers a comprehensive suite of features designed to facilitate seamless resolution management, ensuring that every step, from proposal to finalization, is handled efficiently.
Explore how adam.ai can enhance your corporate resolution process with the following features:
- Real-time content collaboration: Streamline the process of creating corporate resolutions by using adam.ai’s smart note-taking system to record agenda items, actions, decisions, votes, and notes, ensuring a structured and organized approach.
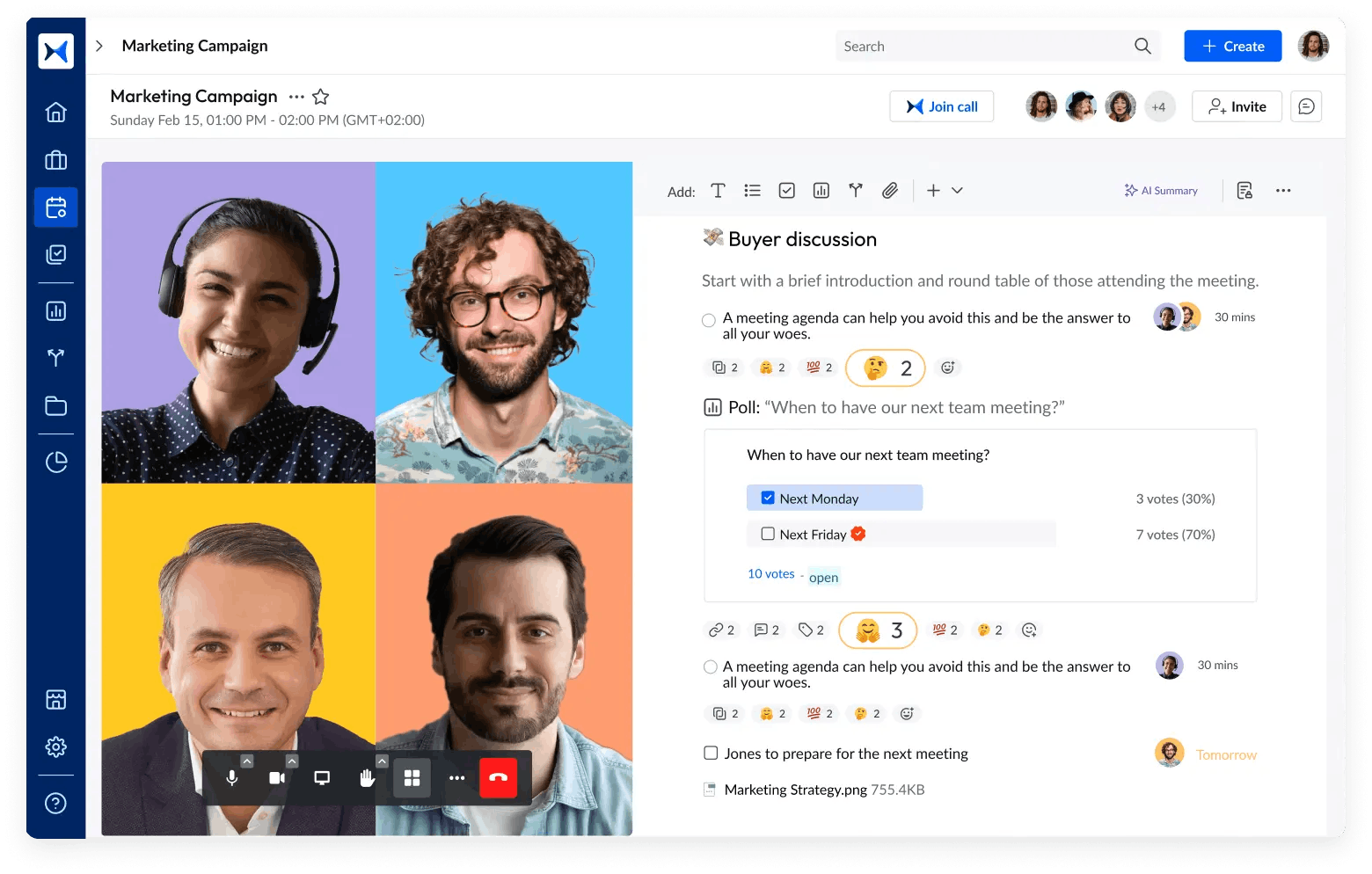
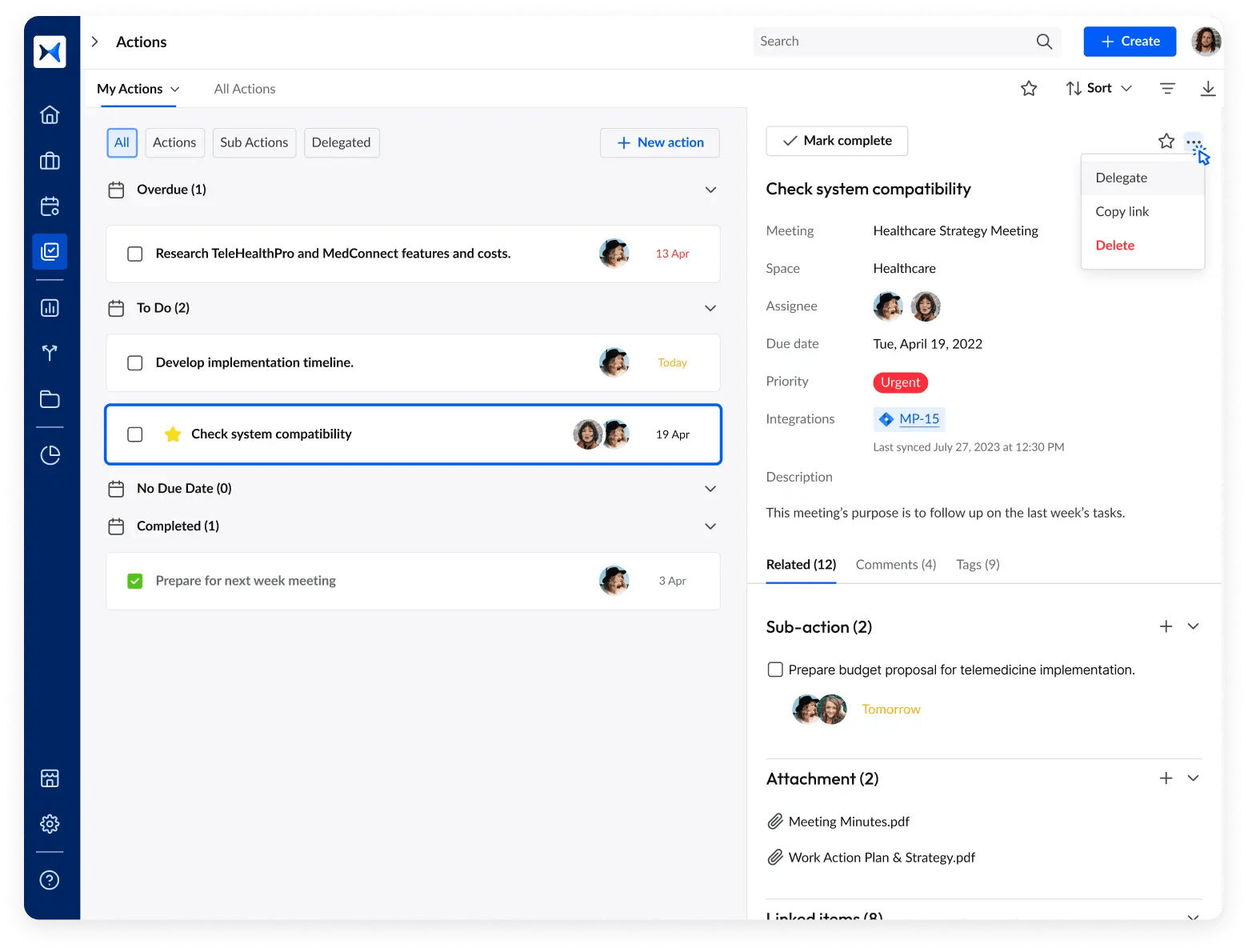
- Action and decision tracking: Enhance accountability and ensure progress by using adam.ai's action and decision tracking feature to follow up on outcomes and follow-through from corporate resolutions.
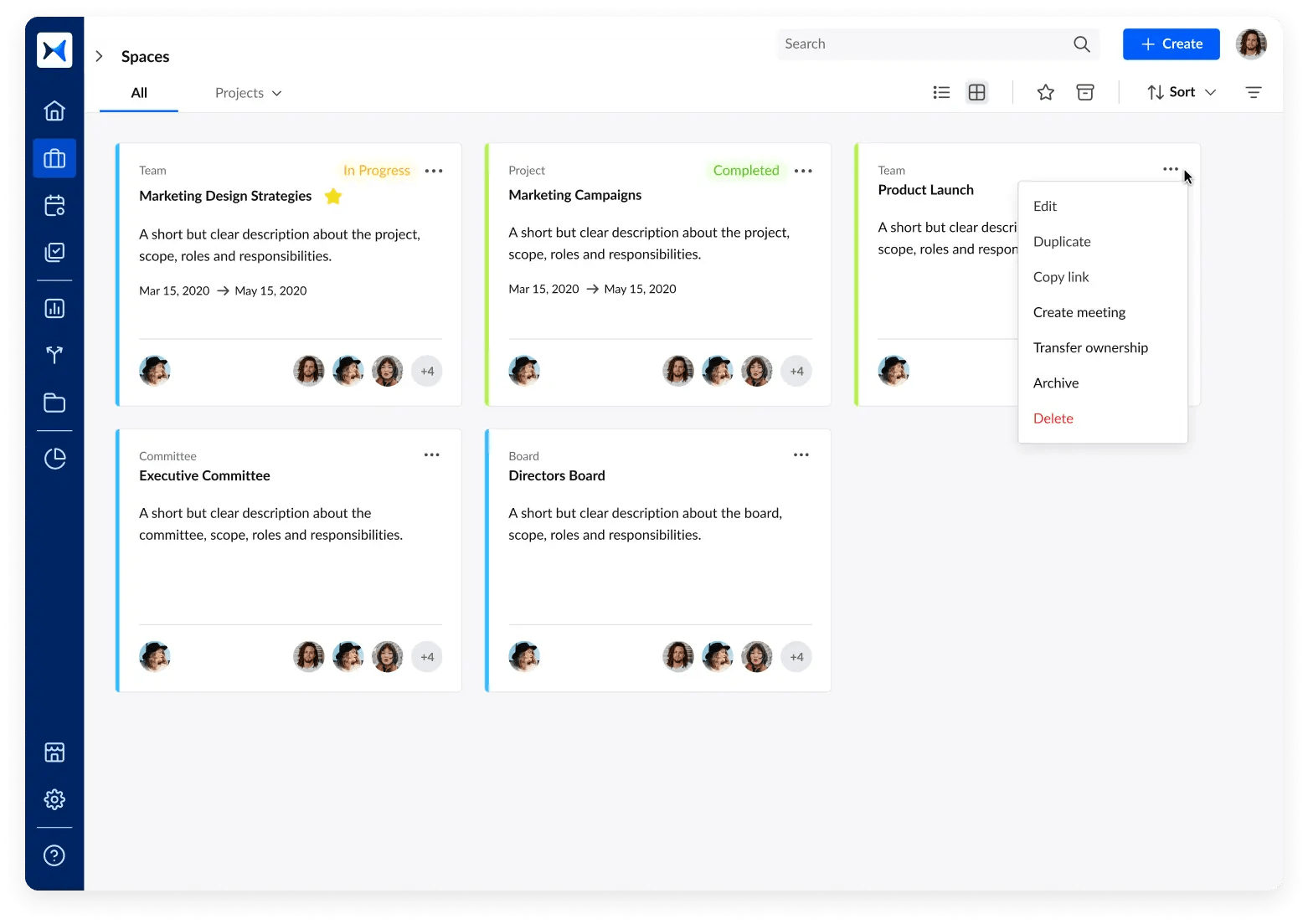
- Multi-space management for meetings and boards: Categorize meetings into specific spaces for various committees, teams, and projects to maintain clear records and focus on corporate resolutions, making strategy management more efficient.
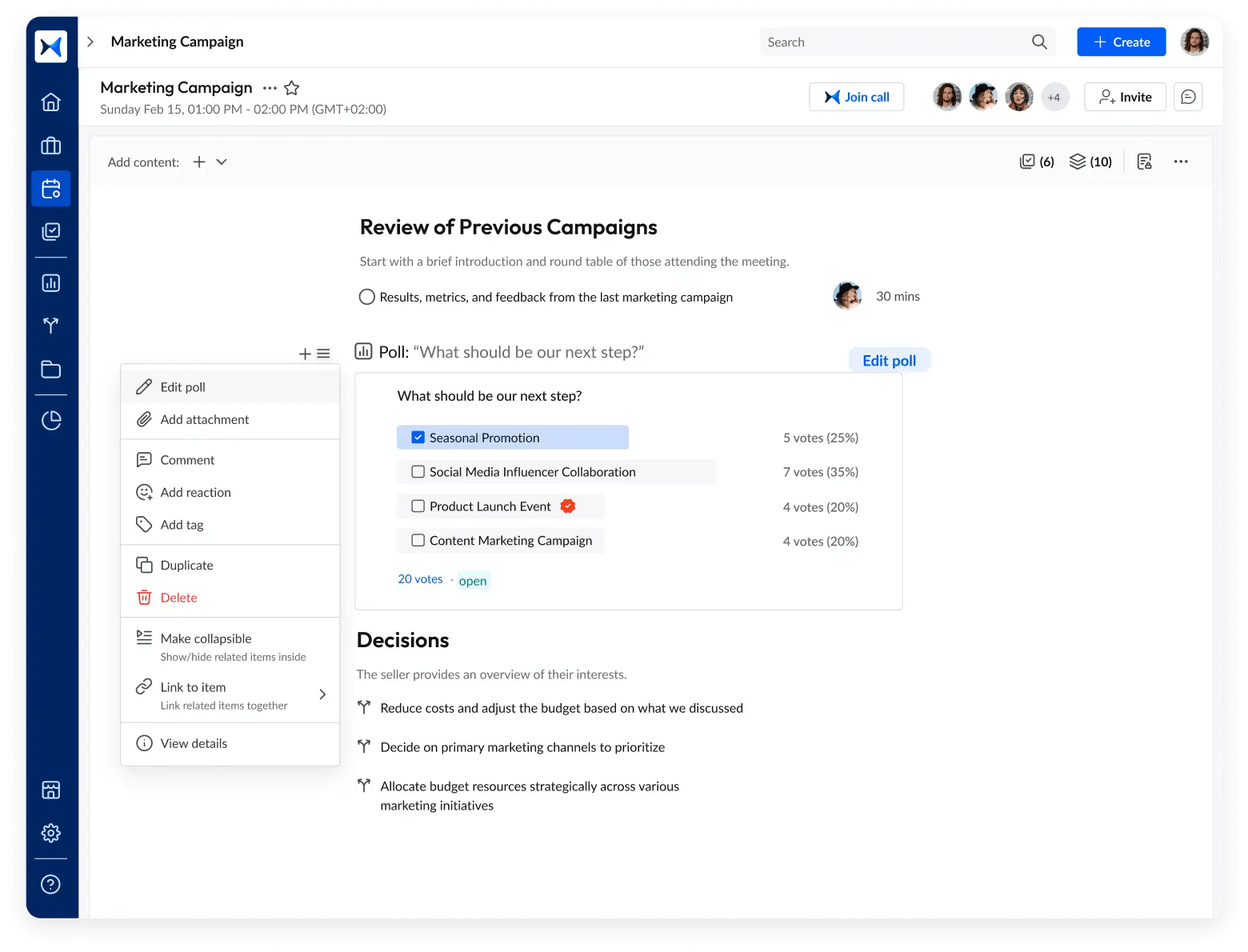
- Voting and decision management: Conduct polls, attach relevant documents directly to the poll, record all decisions related to corporate resolutions with clear rationale, and assign ownership for accountability.
- Automated meeting minutes: Automatically generate and share meeting minutes to ensure transparency and maintain comprehensive records. This feature supports the documentation of all decisions and strategies, making it easier for shareholders to track and review past actions.
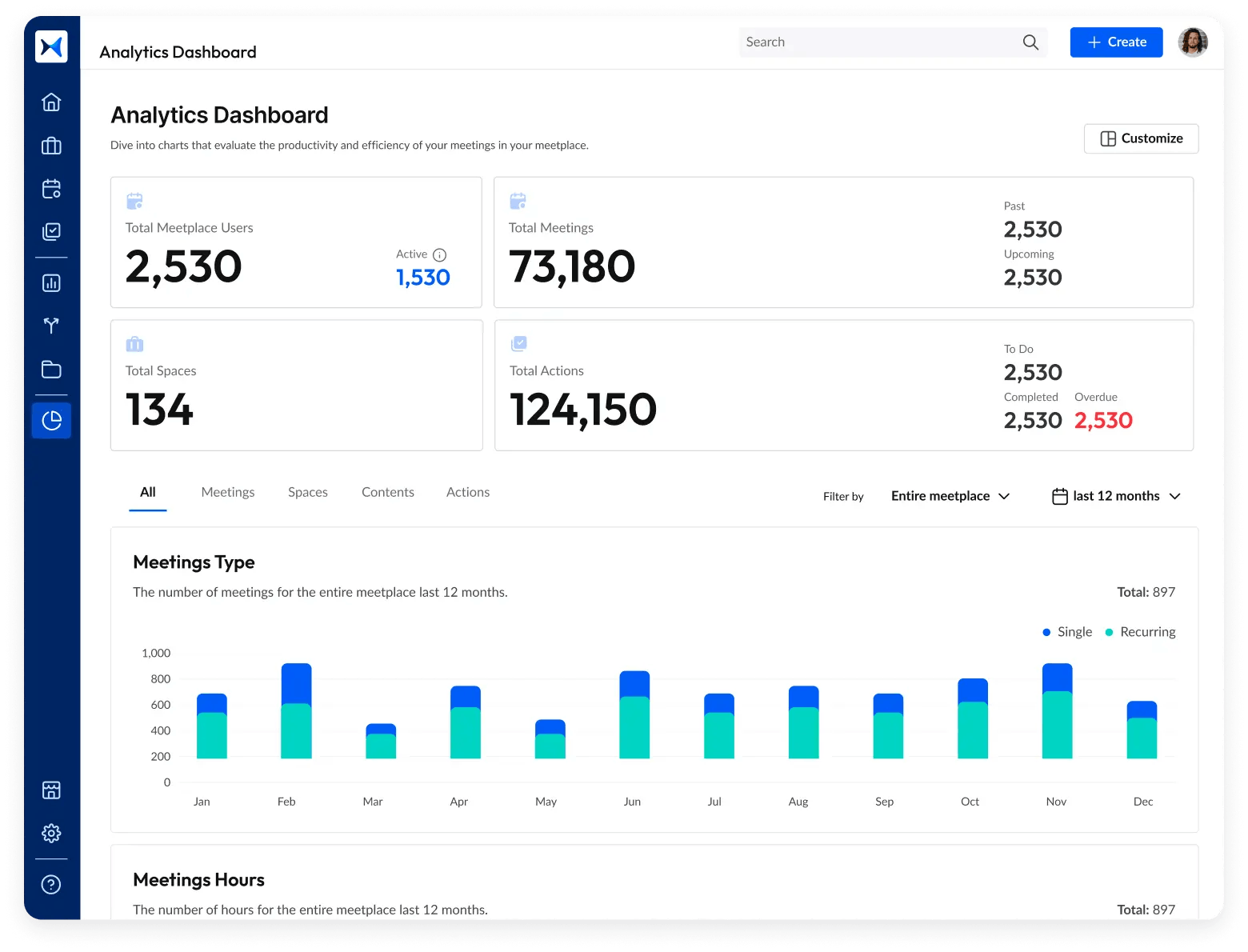
- Analytics dashboard
- Assess participation rates, decision outcomes, and the progress of action items to facilitate smooth and effective meetings, ensuring shareholders stay informed and proactive regarding corporate resolutions.
Transform how you conduct critical meetings—From meticulous preparation to effective execution and insightful follow-up, adam.ai integrates comprehensive analytics, full customization, and intuitive interfaces with powerful meeting management tools.
Easy onboarding. Enterprise-grade security. 24/7 dedicated support.
The bottom line
Optimizing the corporate resolution process is vital for maintaining effective governance and making swift, informed decisions. Utilizing modern tools can ensure transparency and comprehensive documentation of all decisions and strategies, making the resolution process more efficient and accessible.
And while there may be multiple solutions available, here is why adam.ai is the meeting management software platform you can trust:
- adam.ai is one of Atlassian Ventures' portfolio companies.
- In the meeting management software category on G2, adam.ai has been ranked a leader and a high performer for successive quarters in the past years.
- adam.ai has been included in the Forrester Report in the AI-enabled meeting technology landscape.
- adam.ai is trusted and used by powerful teams and organizations worldwide for all types of critical meetings, like board, committee, project management, and business development meetings.
- And most importantly, adam.ai integrates with your existing workflow, is SOC2 compliant, provides dedicated support and success, and has a free trial option.
Subscribe to adam.ai blog
Stay ahead with the latest insights—get our newest blog posts, tips, and updates sent straight to your inbox.